Gene Expression over Time during Cell Transformation Due to Non-Genotoxic Carcinogen Treatment of Bhas 42 Cells
- PMID: 35328637
- PMCID: PMC8954493
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23063216
Gene Expression over Time during Cell Transformation Due to Non-Genotoxic Carcinogen Treatment of Bhas 42 Cells
Abstract
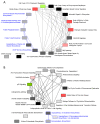
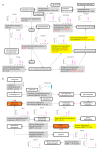
The Bhas 42 cell transformation assay (Bhas 42 CTA) is the first Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)-certificated method used as a specific tool for the detection of the cell-transformation potential of tumor-promoting compounds, including non-genotoxic carcinogens (NGTxCs), as separate from genotoxic carcinogens. This assay offers the great advantage of enabling the phenotypic detection of oncotransformation. A key benefit of using the Bhas 42 CTA in the study of the cell-transformation mechanisms of tumor-promoting compounds, including non-genotoxic carcinogens, is that the cell-transformation potential of the chemical can be detected directly without treatment with a tumor-initiating compound since Bhas 42 cell line was established by transfecting the v-Ha-ras gene into a mouse fibroblast cloned cell line. Here, we analyzed the gene expression over time, using DNA microarrays, in Bhas 42 cells treated with the tumor-promoting compound 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), and NGTxC, with a total of three repeat experiments. This is the first paper to report on gene expression over time during the process of cell transformation with only a tumor-promoting compound. Pathways that were activated or inactivated during the process of cell transformation in the Bhas 42 cells treated with TPA were related not only directly to RAS but also to various pathways in the hallmarks of cancer.
Keywords: 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate; Bhas 42 cells; cell-transformation assay; hallmarks of cancer; non-genotoxic carcinogen; over time; transcriptomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Morita T., Hamada S., Masumura K., Wakata A., Maniwa J., Takasawa H., Yasunaga K., Hashizumef T., Honma M. Evaluation of the sensitivity and specificity of in vivo erythrocyte micronucleus and transgenic rodent gene mutation tests to detect rodent carcinogens. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2016;802:1–29. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2016.03.008. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Combes R.D. Detection of non-genotoxic carcinogens: Major barriers to replacement of the rodent assays. In: Van Zutphen L.F.M., Balls M., editors. Proceedings of the 2nd World Congress on Alternatives and Animal Use in the Life Sciences; Utrecht, The Netherlands. 20–24 October 1996; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier; 1997. pp. 627–634.
-
- Ohmori K., Umeda M., Tanaka N., Takagi T., Yoshimura I., Sasaki K., Asada S., Sakai A., Araki H., Asakura M., et al. An inter-laboratory collaborative study by the Non-Genotoxic Carcinogen Study Group in Japan, on a cell transformation assay for tumour promoters using Bhas 42 cells. Altern. Lab. Anim. 2005;33:619–639. doi: 10.1177/026119290503300616. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

