Interactions between miRNAs and Double-Strand Breaks DNA Repair Genes, Pursuing a Fine-Tuning of Repair
- PMID: 35328651
- PMCID: PMC8954595
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23063231
Interactions between miRNAs and Double-Strand Breaks DNA Repair Genes, Pursuing a Fine-Tuning of Repair
Abstract
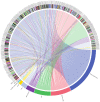
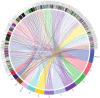
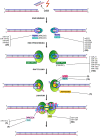
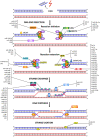
The repair of DNA damage is a crucial process for the correct maintenance of genetic information, thus, allowing the proper functioning of cells. Among the different types of lesions occurring in DNA, double-strand breaks (DSBs) are considered the most harmful type of lesion, which can result in significant loss of genetic information, leading to diseases, such as cancer. DSB repair occurs through two main mechanisms, called non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) and homologous recombination repair (HRR). There is evidence showing that miRNAs play an important role in the regulation of genes acting in NHEJ and HRR mechanisms, either through direct complementary binding to mRNA targets, thus, repressing translation, or by targeting other genes involved in the transcription and activity of DSB repair genes. Therefore, alteration of miRNA expression has an impact on the ability of cells to repair DSBs, which, in turn, affects cancer therapy sensitivity. This latter gives account of the importance of miRNAs as regulators of NHEJ and HRR and places them as a promising target to improve cancer therapy. Here, we review recent reports demonstrating an association between miRNAs and genes involved in NHEJ and HRR. We employed the Web of Science search query TS ("gene official symbol/gene aliases*" AND "miRNA/microRNA/miR-") and focused on articles published in the last decade, between 2010 and 2021. We also performed a data analysis to represent miRNA-mRNA validated interactions from TarBase v.8, in order to offer an updated overview about the role of miRNAs as regulators of DSB repair.
Keywords: DNA repair; double-strand breaks; homologous recombination repair; miRNAs; non-homologous end joining.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of chromatid-break-repair detects a homologous recombination to non-homologous end-joining switch with increasing load of DNA double-strand breaks.Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2021 Jul;867:503372. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2021.503372. Epub 2021 Jun 12. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2021. PMID: 34266628
-
miR-21-mediated Radioresistance Occurs via Promoting Repair of DNA Double Strand Breaks.J Biol Chem. 2017 Feb 24;292(8):3531-3540. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.772392. Epub 2017 Jan 17. J Biol Chem. 2017. Retraction in: J Biol Chem. 2020 May 1;295(18):6250. doi: 10.1074/jbc.W120.013725. PMID: 28096467 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Role for Artemis nuclease in the repair of radiation-induced DNA double strand breaks by alternative end joining.DNA Repair (Amst). 2015 Jul;31:29-40. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2015.04.004. Epub 2015 Apr 25. DNA Repair (Amst). 2015. PMID: 25973742
-
Alternative end-joining repair pathways are the ultimate backup for abrogated classical non-homologous end-joining and homologous recombination repair: Implications for the formation of chromosome translocations.Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2015 Nov;793:166-75. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2015.07.001. Epub 2015 Jul 4. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2015. PMID: 26520387 Review.
-
DNA repair by RNA: Templated, or not templated, that is the question.DNA Repair (Amst). 2016 Aug;44:17-21. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2016.05.002. Epub 2016 May 16. DNA Repair (Amst). 2016. PMID: 27237587 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of AKT Pathway-Targeting miRNAs for Cancer Cell Treatment with Natural Products.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 12;24(4):3688. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043688. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Analysis of miRNA Expression after Whole-Body Irradiation Across Three Strains of Mice.Radiat Res. 2023 Sep 1;200(3):266-280. doi: 10.1667/RADE-23-00007.1. Radiat Res. 2023. PMID: 37527359 Free PMC article.
-
The multifaceted role of microRNAs in colorectal cancer: pathogenesis and therapeutic implications.Noncoding RNA Res. 2025 May 23;14:65-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2025.05.012. eCollection 2025 Oct. Noncoding RNA Res. 2025. PMID: 40535722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The lncRNA DLX6-AS1/miR-16-5p axis regulates autophagy and apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer: A Boolean model of cell death.Noncoding RNA Res. 2023 Aug 10;8(4):605-614. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2023.08.003. eCollection 2023 Dec. Noncoding RNA Res. 2023. PMID: 37767112 Free PMC article.
-
Drug resistance in ovarian cancer: from mechanism to clinical trial.Mol Cancer. 2024 Mar 28;23(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-01967-3. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38539161 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

