Pathophysiological Roles of Actin-Binding Scaffold Protein, Ezrin
- PMID: 35328667
- PMCID: PMC8952289
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23063246
Pathophysiological Roles of Actin-Binding Scaffold Protein, Ezrin
Abstract
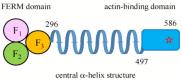
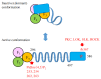
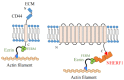
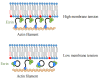
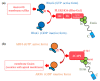
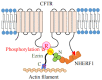
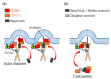
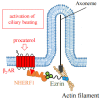
Ezrin is one of the members of the ezrin/radixin/moesin (ERM) family of proteins. It was originally discovered as an actin-binding protein in the microvilli structure about forty years ago. Since then, it has been revealed as a key protein with functions in a variety of fields including cell migration, survival, and signal transduction, as well as functioning as a structural component. Ezrin acts as a cross-linker of membrane proteins or phospholipids in the plasma membrane and the actin cytoskeleton. It also functions as a platform for signaling molecules at the cell surface. Moreover, ezrin is regarded as an important target protein in cancer diagnosis and therapy because it is a key protein involved in cancer progression and metastasis, and its high expression is linked to poor survival in many cancers. Small molecule inhibitors of ezrin have been developed and investigated as candidate molecules that suppress cancer metastasis. Here, we wish to comprehensively review the roles of ezrin from the pathophysiological points of view.
Keywords: G protein; actin; cancer; ciliogenesis; cytoskeleton; ezrin; metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
P-glycoprotein-actin association through ERM family proteins: a role in P-glycoprotein function in human cells of lymphoid origin.Blood. 2002 Jan 15;99(2):641-8. doi: 10.1182/blood.v99.2.641. Blood. 2002. PMID: 11781249
-
Cortical actin organization: lessons from ERM (ezrin/radixin/moesin) proteins.J Biol Chem. 1999 Dec 3;274(49):34507-10. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.49.34507. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10574907 Review. No abstract available.
-
Ezrin: a protein requiring conformational activation to link microfilaments to the plasma membrane in the assembly of cell surface structures.J Cell Sci. 1997 Dec;110 ( Pt 24):3011-8. doi: 10.1242/jcs.110.24.3011. J Cell Sci. 1997. PMID: 9365271 Review.
-
Ezrin, Radixin and Moesin: key regulators of membrane-cortex interactions and signaling.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2011 Aug;23(4):377-82. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2011.04.011. Epub 2011 May 16. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21592758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct involvement of ezrin/radixin/moesin (ERM)-binding membrane proteins in the organization of microvilli in collaboration with activated ERM proteins.J Cell Biol. 1999 Jun 28;145(7):1497-509. doi: 10.1083/jcb.145.7.1497. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10385528 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Extracellular Vesicles and Tunnelling Nanotubes as Mediators of Prostate Cancer Intercellular Communication.Biomolecules. 2024 Dec 27;15(1):23. doi: 10.3390/biom15010023. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39858418 Free PMC article.
-
Mass Spectrometric-Based Proteomics for Biomarker Discovery in Osteosarcoma: Current Status and Future Direction.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 28;23(17):9741. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179741. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CYLD Maintains Retinal Homeostasis by Deubiquitinating ENKD1 and Promoting the Phagocytosis of Photoreceptor Outer Segments.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Dec;11(45):e2404067. doi: 10.1002/advs.202404067. Epub 2024 Oct 7. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39373352 Free PMC article.
-
Ezrin expression in female reproductive tissues: A review of regulation and pathophysiological implications.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Mar 8;11:1125881. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1125881. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36968198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone H3K18 and Ezrin Lactylation Promote Renal Dysfunction in Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Jul;11(28):e2307216. doi: 10.1002/advs.202307216. Epub 2024 May 20. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38767134 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

