A Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals That HSP90AB1 Is Involved in the Immune and Inflammatory Responses to Porcine Deltacoronavirus Infection
- PMID: 35328701
- PMCID: PMC8953809
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23063280
A Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals That HSP90AB1 Is Involved in the Immune and Inflammatory Responses to Porcine Deltacoronavirus Infection
Abstract
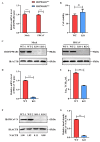
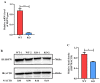
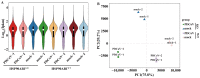
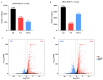
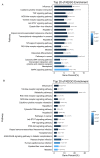
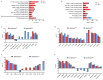
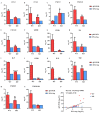
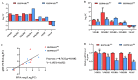
PDCoV is an emerging enteropathogenic coronavirus that mainly causes acute diarrhea in piglets, seriously affecting pig breeding industries worldwide. To date, the molecular mechanisms of PDCoV-induced immune and inflammatory responses or host responses in LLC-PK cells in vitro are not well understood. HSP90 plays important roles in various viral infections. In this study, HSP90AB1 knockout cells (HSP90AB1KO) were constructed and a comparative transcriptomic analysis between PDCoV-infected HSP90AB1WT and HSP90AB1KO cells was conducted using RNA sequencing to explore the effect of HSP90AB1 on PDCoV infection. A total of 1295 and 3746 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified in PDCoV-infected HSP90AB1WT and HSP90AB1KO cells, respectively. Moreover, most of the significantly enriched pathways were related to immune and inflammatory response-associated pathways upon PDCoV infection. The DEGs enriched in NF-κB pathways were specifically detected in HSP90AB1WT cells, and NF-κB inhibitors JSH-23, SC75741 and QNZ treatment reduced PDCoV infection. Further research revealed most cytokines associated with immune and inflammatory responses were upregulated during PDCoV infection. Knockout of HSP90AB1 altered the upregulated levels of some cytokines. Taken together, our findings provide new insights into the host response to PDCoV infection from the transcriptome perspective, which will contribute to illustrating the molecular basis of the interaction between PDCoV and HSP90AB1.
Keywords: HSP90AB1; PDCoV; immune and inflammatory response; transcriptomic analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
HSP90AB1 is a host factor that promotes porcine deltacoronavirus replication.J Biol Chem. 2024 Jan;300(1):105536. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105536. Epub 2023 Dec 12. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38092149 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Transcriptome Profiling of Human and Pig Intestinal Epithelial Cells after Porcine Deltacoronavirus Infection.Viruses. 2021 Feb 13;13(2):292. doi: 10.3390/v13020292. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33668405 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation, characterization and transcriptome analysis of porcine deltacoronavirus strain HNZK-02 from Henan Province, China.Mol Immunol. 2021 Jun;134:86-99. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2021.03.006. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Mol Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33740580
-
Porcine deltacoronavirus infection: Etiology, cell culture for virus isolation and propagation, molecular epidemiology and pathogenesis.Virus Res. 2016 Dec 2;226:50-59. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.04.009. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Virus Res. 2016. PMID: 27086031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Research Advances in the Porcine Deltacoronavirus].Bing Du Xue Bao. 2016 Mar;32(2):243-8. Bing Du Xue Bao. 2016. PMID: 27396171 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
TLR7 promotes skin inflammation via activating NFκB-mTORC1 axis in rosacea.PeerJ. 2023 Sep 26;11:e15976. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15976. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37780385 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Analysis of LLC-PK Cells Single or Coinfected with Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus and Porcine Deltacoronavirus.Viruses. 2023 Dec 31;16(1):74. doi: 10.3390/v16010074. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 38257774 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant Expressions of PSMD14 in Tumor Tissue are the Potential Prognostic Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Curative Resection.Curr Genomics. 2023 Dec 28;24(6):368-384. doi: 10.2174/0113892029277262231108105441. Curr Genomics. 2023. PMID: 38327651 Free PMC article.
-
Role of heat shock protein 90 as an antiviral target for swine enteric coronaviruses.Virus Res. 2023 May;329:199103. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2023.199103. Epub 2023 Mar 28. Virus Res. 2023. PMID: 36963723 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation, phylogenetics, and characterization of a new PDCoV strain that affects cellular gene expression in human cells.Front Microbiol. 2025 Mar 26;16:1534907. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1534907. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40207165 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

