Tricyclodecan-9-yl-Xanthogenate (D609): Mechanism of Action and Pharmacological Applications
- PMID: 35328726
- PMCID: PMC8954530
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23063305
Tricyclodecan-9-yl-Xanthogenate (D609): Mechanism of Action and Pharmacological Applications
Abstract
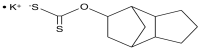
Tricyclodecan-9-yl xanthogenate (D609) is a synthetic tricyclic compound possessing a xanthate group. This xanthogenate compound is known for its diverse pharmacological properties. Over the last three decades, many studies have reported the biological activities of D609, including antioxidant, antiapoptotic, anticholinergic, anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, anti-viral, anti-proliferative, and neuroprotective activities. Its mechanism of action is extensively attributed to its ability to cause the competitive inhibition of phosphatidylcholine (PC)-specific phospholipase C (PC-PLC) and sphingomyelin synthase (SMS). The inhibition of PCPLC or SMS affects secondary messengers with a lipidic nature, i.e., 1,2-diacylglycerol (DAG) and ceramide. Various in vitro/in vivo studies suggest that PCPLC and SMS inhibition regulate the cell cycle, block cellular proliferation, and induce differentiation. D609 acts as a pro-inflammatory cytokine antagonist and diminishes Aβ-stimulated toxicity. PCPLC enzymatic activity essentially requires Zn2+, and D609 might act as a potential chelator of Zn2+, thereby blocking PCPLC enzymatic activity. D609 also demonstrates promising results in reducing atherosclerotic plaque formation, post-stroke cerebral infarction, and cancer progression. The present compilation provides a comprehensive mechanistic insight into D609, including its chemistry, mechanism of action, and regulation of various pharmacological activities.
Keywords: cellular proliferation; ceramide; pharmacological properties; tricyclodecan-9-yl xanthogenate (D609).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Eurtivong C., Pilkington L.I., van Rensburg M., White R.M., Bar H.K., Rees S., Paulin E.K., Xu C.S., Sharma N., Leung I.K.H., et al. Discovery of novel phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C drug-like inhibitors as potential anticancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020;187:111919. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111919. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Podo F., Paris L., Cecchetti S., Spadaro F., Abalsamo L., Ramoni C., Ricci A., Pisanu M.E., Sardanelli F., Canese R., et al. Activation of phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C in breast and ovarian cancer: Impact on MRS-detected choline metabolic profile and perspectives for targeted therapy. Front. Oncol. 2016;6:171. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2016.00171. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Milhas D., Andrieu-Abadie N., Levade T., Benoist H., Ségui B. The tricyclodecan-9-yl-xanthogenate D609 triggers ceramide increase and enhances FasL-induced caspase-dependent and-independent cell death in T lymphocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012;13:8834–8852. doi: 10.3390/ijms13078834. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources