CCL2 Inhibition of Pro-Resolving Mediators Potentiates Neuroinflammation in Astrocytes
- PMID: 35328727
- PMCID: PMC8949263
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23063307
CCL2 Inhibition of Pro-Resolving Mediators Potentiates Neuroinflammation in Astrocytes
Abstract
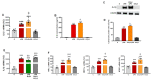
The chemokine CCL2 participates in multiple neuroinflammatory processes, mainly through the recruitment of glial cells. However, CCL2 has also been proven to exert different types of actions on these cells, including the modification of their response to inflammatory stimuli. In the present study we analyzed the effect of CCL2 on the resolution of inflammation in astrocytes. We observed that genetic removal of CCL2 increases the expression of the enzymes responsible for the synthesis of specialized pro-resolving mediators arachidonate 15-lipoxygenase and arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase in the brain cortex of 5xFAD mice. The expression of FPR2 receptor, known to mediate the activity of pro-resolving mediators was also increased in mice lacking CCL2.The downregulation of these proteins by CCL2 was also observed in cultured astrocytes. This suggests that CCL2 inhibition of the resolution of inflammation could facilitate the progression of neuroinflammatory processes. The production of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1beta by astrocytes was analyzed, and allowed us to confirm that CCL2 potentiates the activation of astrocytes trough the inhibition of pro-resolving pathways mediated by Resolvin D1. In addition, the analysis of the expression of TNFalpha, MIP1alpha and NOS2 further confirmed CCL2 inhibition of inflammation resolution in astrocytes.
Keywords: CCL2; LPS; MCP-1; astrocytes; inflammation; resolvin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
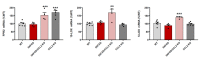

Similar articles
-
CCL2 modulates cytokine production in cultured mouse astrocytes.J Neuroinflammation. 2010 Oct 14;7:67. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-7-67. J Neuroinflammation. 2010. PMID: 20942978 Free PMC article.
-
Glia Maturation Factor and Mast Cell-Dependent Expression of Inflammatory Mediators and Proteinase Activated Receptor-2 in Neuroinflammation.J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;66(3):1117-1129. doi: 10.3233/JAD-180786. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018. PMID: 30372685 Free PMC article.
-
Huperzine A inhibits CCL2 production in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice and in cultured astrocyte.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2013 Jul-Sep;26(3):757-64. doi: 10.1177/039463201302600320. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24067473
-
Pharmacological modulation of cytokines correlating neuroinflammatory cascades in epileptogenesis.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Feb;49(2):1437-1452. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06896-8. Epub 2021 Nov 9. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 34751915 Review.
-
The interaction of lipocalin-2 and astrocytes in neuroinflammation: mechanisms and therapeutic application.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 12;15:1358719. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1358719. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38533497 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic IL-21 drives neuroinflammation and promotes lipid accumulation in microglia.Immun Ageing. 2025 Apr 29;22(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12979-025-00510-2. Immun Ageing. 2025. PMID: 40301833 Free PMC article.
-
Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators in Neuroinflammation: Overview of Studies and Perspectives of Clinical Applications.Molecules. 2022 Jul 28;27(15):4836. doi: 10.3390/molecules27154836. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35956787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astrocyte-mediated inflammatory responses in traumatic brain injury: mechanisms and potential interventions.Front Immunol. 2025 May 8;16:1584577. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1584577. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40406119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Atypical Chemokine Receptors in Neuroinflammation and Neurodegenerative Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 18;24(22):16493. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216493. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19-induced neurological symptoms: focus on the role of metal ions.Inflammopharmacology. 2023 Apr;31(2):611-631. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01176-2. Epub 2023 Mar 9. Inflammopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 36892679 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gutierrez I.L., Gonzalez-Prieto M., Caso J.R., Garcia-Bueno B., Leza J.C., Madrigal J.L.M. Reboxetine Treatment Reduces Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration in the 5xFAD Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease: Role of CCL2. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019;56:8628–8642. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-01695-6. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

