Recent Progress on the Salt Tolerance Mechanisms and Application of Tamarisk
- PMID: 35328745
- PMCID: PMC8950588
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23063325
Recent Progress on the Salt Tolerance Mechanisms and Application of Tamarisk
Abstract
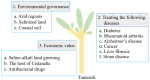
Salinized soil is a major environmental stress affecting plant growth and development. Excessive salt in the soil inhibits the growth of most plants and even threatens their survival. Halophytes are plants that can grow and develop normally on saline-alkali soil due to salt tolerance mechanisms that emerged during evolution. For this reason, halophytes are used as pioneer plants for improving and utilizing saline land. Tamarisk, a family of woody halophytes, is highly salt tolerant and has high economic value. Understanding the mechanisms of salt tolerance in tamarisk and identifying the key genes involved are important for improving saline land and increasing the salt tolerance of crops. Here, we review recent advances in our understanding of the salt tolerance mechanisms of tamarisk and the economic and medicinal value of this halophyte.
Keywords: application value; halophyte; salinization; salt tolerant; tamarisk.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Adaptive Mechanisms of Halophytes and Their Potential in Improving Salinity Tolerance in Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 3;22(19):10733. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910733. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergistic potential of halophytes and halophilic/halotolerant plant growth-promoting bacteria in saline soil remediation: Adaptive mechanisms, challenges, and sustainable solutions.Microbiol Res. 2025 Sep;298:128227. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2025.128227. Epub 2025 May 22. Microbiol Res. 2025. PMID: 40440870 Review.
-
Utilization of halophytes in saline agriculture and restoration of contaminated salinized soils from genes to ecosystem: Suaeda salsa as an example.Mar Pollut Bull. 2023 Dec;197:115728. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2023.115728. Epub 2023 Oct 31. Mar Pollut Bull. 2023. PMID: 37918144 Review.
-
Plant salt tolerance: adaptations in halophytes.Ann Bot. 2015 Feb;115(3):327-31. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcu267. Ann Bot. 2015. PMID: 25844430 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in the Study and Use of Seawater Vegetables.J Agric Food Chem. 2020 Jun 3;68(22):5998-6006. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c00346. Epub 2020 May 19. J Agric Food Chem. 2020. PMID: 32374599 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic analyses provide insights into the evolution and salinity adaptation of halophyte Tamarix chinensis.Gigascience. 2022 Dec 28;12:giad053. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giad053. Epub 2023 Jul 26. Gigascience. 2022. PMID: 37494283 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in Metabolic Characteristics of Rhizosphere Fungal Community of Typical Arboreal, Shrubby and Herbaceous Species in Oasis of Arid Region.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Aug 10;10(8):565. doi: 10.3390/jof10080565. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39194891 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Amino Acids in the Roots of Tamarix ramosissima by Application of Exogenous Potassium (K+) under NaCl Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 19;23(16):9331. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169331. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012595 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the Antioxidant Mechanism of Tamarix ramosissima Roots under NaCl Stress Based on Physiology, Transcriptomic and Metabolomic.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Nov 28;11(12):2362. doi: 10.3390/antiox11122362. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36552570 Free PMC article.
-
The role of WRKY transcription factors in exogenous potassium (K+) response to NaCl stress in Tamarix ramosissima.Front Genet. 2023 Nov 20;14:1274288. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1274288. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 38054027 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

