Climate Change Impact on Wheat Performance-Effects on Vigour, Plant Traits and Yield from Early and Late Drought Stress in Diverse Lines
- PMID: 35328754
- PMCID: PMC8950129
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23063333
Climate Change Impact on Wheat Performance-Effects on Vigour, Plant Traits and Yield from Early and Late Drought Stress in Diverse Lines
Abstract
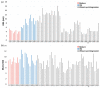
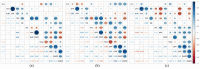
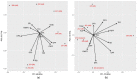
Global climate change is threatening wheat productivity; improved yield under drought conditions is urgent. Here, diverse spring-wheat lines (modern, old and wheat-rye introgressions) were examined in an image-based early-vigour assay and a controlled-conditions (Biotron) trial that evaluated 13 traits until maturity. Early root vigour was significantly higher in the old Swedish lines (root length 8.50 cm) and introgressed lines with 1R (11.78 cm) and 1RS (9.91 cm) than in the modern (4.20 cm) and 2R (4.67 cm) lines. No significant correlation was noted between early root and shoot vigour. A higher yield was obtained under early drought stress in the 3R genotypes than in the other genotype groups, while no clear patterns were noted under late drought. Evaluating the top 10% of genotypes in terms of the stress-tolerance index for yield showed that root biomass, grains and spikes per plant were accountable for tolerance to early drought, while 1000-grain weight and flag-leaf area were accountable for tolerance to late drought. Early root vigour was determined as an important focus trait of wheat breeding for tolerance to climate-change-induced drought. The responsible genes for the trait should be searched for in these diverse lines. Additional drought-tolerance traits determined here need further elaboration to identify the responsible genes.
Keywords: drought; early vigour; image-based phenotyping; spring wheat; stress-tolerance index; yield performance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
-
- Shiferaw B., Smale M., Braun H.-J., Duveiller E., Reynolds M., Muricho G. Crops that feed the world 10. Past successes and future challenges to the role played by wheat in global food security. Food Secur. 2013;5:291–317. doi: 10.1007/s12571-013-0263-y. - DOI
-
- Cataldo E., Salvi L., Paoli F., Fucile M., Mattii G.B. Effect of Agronomic Techniques on Aroma Composition of White Grapevines: A Review. Agronomy. 2021;11:2027. doi: 10.3390/agronomy11102027. - DOI
-
- Lambers H., Chapin F.S., III, Pons T.L. Plant Physiological Ecology. Springer Science & Business Media; New York, NY, USA: 2008.
-
- Fischer R., Maurer R. Drought resistance in spring wheat cultivars. I. Grain yield responses. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1978;29:897–912. doi: 10.1071/AR9780897. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

