Structural Plasticity of the Hippocampus in Neurodegenerative Diseases
- PMID: 35328770
- PMCID: PMC8955928
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23063349
Structural Plasticity of the Hippocampus in Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
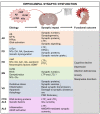
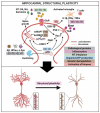
Neuroplasticity is the capacity of neural networks in the brain to alter through development and rearrangement. It can be classified as structural and functional plasticity. The hippocampus is more susceptible to neuroplasticity as compared to other brain regions. Structural modifications in the hippocampus underpin several neurodegenerative diseases that exhibit cognitive and emotional dysregulation. This article reviews the findings of several preclinical and clinical studies about the role of structural plasticity in the hippocampus in neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, and multiple sclerosis. In this study, literature was surveyed using Google Scholar, PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus, to review the mechanisms that underlie the alterations in the structural plasticity of the hippocampus in neurodegenerative diseases. This review summarizes the role of structural plasticity in the hippocampus for the etiopathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases and identifies the current focus and gaps in knowledge about hippocampal dysfunctions. Ultimately, this information will be useful to propel future mechanistic and therapeutic research in neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: hippocampal function; neurodegenerative diseases; neuroplasticity; structural plasticity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Developmental neuroplasticity and the origin of neurodegenerative diseases.World J Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Dec;17(8):587-599. doi: 10.3109/15622975.2013.797104. Epub 2013 May 24. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 23705632 Review.
-
Recent Advances on the Role of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 19;23(12):6827. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126827. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35743271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Particulate matter exposure and neurodegenerative diseases: A comprehensive update on toxicity and mechanisms.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023 Nov 1;266:115565. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115565. Epub 2023 Oct 11. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023. PMID: 37832485 Review.
-
A review on nonviral, nonbacterial infectious agents toxicity involved in neurodegenerative diseases.Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2023 Dec;13(6):351-369. doi: 10.2217/nmt-2023-0004. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2023. PMID: 38357803 Review.
-
Synapses in neurodegenerative diseases.BMB Rep. 2017 May;50(5):237-246. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2017.50.5.038. BMB Rep. 2017. PMID: 28270301 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic-Based Studies on Memory Formation in Normal and Neurodegenerative Disease-Affected Brains.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1443:129-158. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-50624-6_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38409419 Review.
-
Changes in the Neuronal Architecture of the Hippocampus in a 6-Hydroxydopamine-Lesioned Rat Model of Parkinson Disease.Int Neurourol J. 2022 Nov;26(Suppl 2):S94-105. doi: 10.5213/inj.2244252.126. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Int Neurourol J. 2022. PMID: 36503212 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic factors associated with substance use disorder relapse: A critical review.Addict Behav Rep. 2024 Oct 30;20:100569. doi: 10.1016/j.abrep.2024.100569. eCollection 2024 Dec. Addict Behav Rep. 2024. PMID: 39553284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the spectrum of non-motor symptoms in multiple sclerosis: insights from animal models.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Jan;19(1):84-91. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.375307. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 37488849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regional hippocampal atrophy reflects memory impairment in patients with early relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis.J Neurol. 2024 Aug;271(8):4897-4908. doi: 10.1007/s00415-024-12290-8. Epub 2024 May 14. J Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38743090 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Das S., Sadanandappa M.K., Dervan A., Larkin A., Lee J.A., Sudhakaran I.P., Priya R., Heidari R., Holohan E.E., Pimentel A., et al. Plasticity of local GABAergic interneurons drives olfactory habituation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2011;108:E646–E654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1106411108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

