Impact of Endocrine Disruptors upon Non-Genetic Inheritance
- PMID: 35328771
- PMCID: PMC8950994
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23063350
Impact of Endocrine Disruptors upon Non-Genetic Inheritance
Abstract
Similar to environmental factors, EDCs (endocrine-disrupting chemicals) can influence gene expression without modifying the DNA sequence. It is commonly accepted that the transgenerational inheritance of parentally acquired traits is conveyed by epigenetic alterations also known as "epimutations". DNA methylation, acetylation, histone modification, RNA-mediated effects and extracellular vesicle effects are the mechanisms that have been described so far to be responsible for these epimutations. They may lead to the transgenerational inheritance of diverse phenotypes in the progeny when they occur in the germ cells of an affected individual. While EDC-induced health effects have dramatically increased over the past decade, limited effects on sperm epigenetics have been described. However, there has been a gain of interest in this issue in recent years. The gametes (sperm and oocyte) represent targets for EDCs and thus a route for environmentally induced changes over several generations. This review aims at providing an overview of the epigenetic mechanisms that might be implicated in this transgenerational inheritance.
Keywords: embryo; endocrine-disrupting chemicals; epigenetics; non-genetic inheritance; oocyte; sperm; transgenerational inheritance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

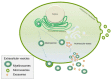
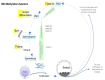
References
-
- Zoeller R.T., Brown T.R., Doan L.L., Gore A.C., Skakkebaek N.E., Soto A.M., Woodruff T.J., Vom Saal F.S. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals and Public Health Protection: A Statement of Principles from The Endocrine Society. Endocrinology. 2012;153:4097–4110. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-1422. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

