Long-Term Effect of Porcine Brain Enzyme Hydrolysate Intake on Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment in Rats
- PMID: 35328781
- PMCID: PMC8951530
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23063361
Long-Term Effect of Porcine Brain Enzyme Hydrolysate Intake on Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment in Rats
Abstract
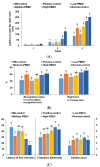
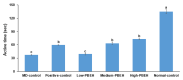
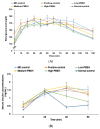
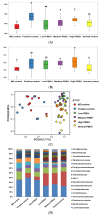
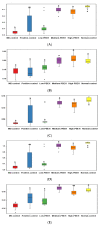
No study has revealed the effect of porcine brain enzyme hydrolysate (PBEH) on memory impairment. We aimed to examine the hypothesis that PBEH intake modulates memory deficits and cognitive behavior in scopolamine (SC)-induced amnesia rats, and its mechanism, including gut microbiota changes, was determined. Sprague-Dawley male rats had intraperitoneal injections of SC (2 mg/kg body weight/day) at 30 min after daily feeding of casein (MD-control), PBEH (7 mg total nitrogen/mL) at 0.053 mL (Low-PBEH), 0.159 mL (Medium-PBEH), 0.478 mL (High-PBEH), or 10 mg donepezil (Positive-control) per kilogram body weight per day through a feeding needle for six weeks. The Normal-control rats had casein feeding without SC injection. PBEH dose-dependently protected against memory deficits determined by passive avoidance test, Y-maze, water-maze, and novel object recognition test in SC-induced rats compared to the MD-control. The High-PBEH group had a similar memory function to the Positive-control group. Systemic insulin resistance determined by HOMA-IR was lower in the PBEH groups than in the Normal-control but not the Positive-control. In parallel with systemic insulin resistance, decreased cholesterol and increased glycogen contents in the hippocampus in the Medium-PBEH and High-PBEH represented reduced brain insulin resistance. PBEH intake prevented the increment of serum TNF-α and IL-1β concentrations in the SC-injected rats. Hippocampal lipid peroxide and TNF-α contents and mRNA TNF-α and IL-1β expression were dose-dependently reduced in PBEH and Positive-control. PBEH decreased the hippocampal acetylcholinesterase activity compared to the MD-control, but not as much as the Positive-control. PBEH intake increased the α-diversity of the gut microbiota compared to the MD-control, and the gut microbiota community was separated from MD-control. In metagenome function analysis, PBEH increased the energy metabolism-related pathways of the gut microbiota, including citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, glycolysis, and amino acid metabolism, which were lower in the MD-control than the Normal-control. In conclusion, alleviated memory deficit by PBEH was associated potentially with not only reducing acetylcholinesterase activity but also improving brain insulin resistance and neuroinflammation potentially through modulating gut microbiota. PBEH intake (1.5-4.5 mL of 7 mg total nitrogen/mL for human equivalent) can be a potential therapeutic agent for improving memory impairment.
Keywords: acetylcholinesterase; insulin resistance; memory deficit; porcine brain enzyme hydrolysates; scopolamine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Moderate capsaicin-containing kochujang alleviates memory impairment through the gut-brain axis in rats with scopolamine-induced amnesia.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Sep;178:117091. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117091. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 39024840
-
Porcine Brain Enzyme Hydrolysate Enhances Immune Function and Antioxidant Defense via Modulation of Gut Microbiota in a Cyclophosphamide-Induced Immunodeficiency Model.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Apr 17;13(4):476. doi: 10.3390/antiox13040476. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38671923 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Cucurbita maxima extract against scopolamine-induced amnesia in rats: implication of tumour necrosis factor alpha.Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 2014 Sep-Oct;69(9-10):407-17. doi: 10.5560/znc.2014-0003. Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 2014. PMID: 25711042
-
Sobrerol Improves Memory Impairment in the Scopolamine-Induced Amnesia Mouse Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 12;26(10):4613. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104613. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429757 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanisms of learning and memory impairment caused by nonylphenol: a narrative review based on in vivo and in vitro studies.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023 Jan;30(3):5530-5539. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-24278-w. Epub 2022 Nov 25. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023. PMID: 36434456 Review.
Cited by
-
Zeaxanthin and Lutein Ameliorate Alzheimer's Disease-like Pathology: Modulation of Insulin Resistance, Neuroinflammation, and Acetylcholinesterase Activity in an Amyloid-β Rat Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 11;25(18):9828. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189828. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337316 Free PMC article.
-
Fecal Bacterial Community and Metagenome Function in Asians with Type 2 Diabetes, According to Enterotypes.Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 21;10(11):2998. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10112998. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36428566 Free PMC article.
-
Network Pharmacology-Guided Evaluation of Ginger and Cornelian Cherry Extracts Against Depression and Metabolic Dysfunction in Estrogen-Deficient Chronic Stressed Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 18;26(10):4829. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104829. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429970 Free PMC article.
-
A Systems Biology Approach to Memory Health: Integrating Network Pharmacology, Gut Microbiota, and Multi-Omics for Health Functional Foods.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 12;26(14):6698. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146698. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40724948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective Effect of Nosustrophine in a 3xTg Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Sep 15;16(9):1306. doi: 10.3390/ph16091306. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37765114 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tota S., Nath C., Najmi A.K., Shukla R., Hanif K. Inhibition of central angiotensin-converting enzyme ameliorates scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice: Role of cholinergic neurotransmission, cerebral blood flow and brain energy metabolism. Behav. Brain Res. 2012;232:66–76. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2012.03.015. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

