Versatile Oral Insulin Delivery Nanosystems: From Materials to Nanostructures
- PMID: 35328783
- PMCID: PMC8952690
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23063362
Versatile Oral Insulin Delivery Nanosystems: From Materials to Nanostructures
Abstract
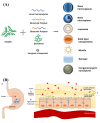
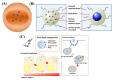
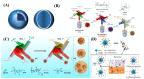
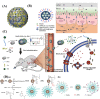
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disease characterized by lack of insulin in the body leading to failure of blood glucose regulation. Diabetes patients usually need frequent insulin injections to maintain normal blood glucose levels, which is a painful administration manner. Long-term drug injection brings great physical and psychological burden to diabetic patients. In order to improve the adaptability of patients to use insulin and reduce the pain caused by injection, the development of oral insulin formulations is currently a hot and difficult topic in the field of medicine and pharmacy. Thus, oral insulin delivery is a promising and convenient administration method to relieve the patients. However, insulin as a peptide drug is prone to be degraded by digestive enzymes. In addition, insulin has strong hydrophilicity and large molecular weight and extremely low oral bioavailability. To solve these problems in clinical practice, the oral insulin delivery nanosystems were designed and constructed by rational combination of various nanomaterials and nanotechnology. Such oral nanosystems have the advantages of strong adaptability, small size, convenient processing, long-lasting pharmaceutical activity, and drug controlled-release, so it can effectively improve the oral bioavailability and efficacy of insulin. This review summarizes the basic principles and recent progress in oral delivery nanosystems for insulin, including physiological absorption barrier of oral insulin and the development of materials to nanostructures for oral insulin delivery nanosystems.
Keywords: absorption barrier; bioavailability; nanodrug delivery system; oral insulin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Therapeutic nanosystems for oral administration of insulin.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2014;15(7):620-8. doi: 10.2174/1389201015666140915150826. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25219867 Review.
-
Materials and structure of polysaccharide-based delivery carriers for oral insulin: A review.Carbohydr Polym. 2024 Jan 1;323:121364. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.121364. Epub 2023 Sep 9. Carbohydr Polym. 2024. PMID: 37940264 Review.
-
Nano-based drug delivery system enhances the oral absorption of lipophilic drugs with extensive presystemic metabolism.Curr Drug Metab. 2012 Oct;13(8):1110-8. doi: 10.2174/138920012802850100. Curr Drug Metab. 2012. PMID: 22380010 Review.
-
New ways of insulin delivery.Int J Clin Pract Suppl. 2010 Feb;(166):29-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2009.02276.x. Int J Clin Pract Suppl. 2010. PMID: 20377662 Review.
-
Investigation Of Vitamin B12-Modified Amphiphilic Sodium Alginate Derivatives For Enhancing The Oral Delivery Efficacy Of Peptide Drugs.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Sep 20;14:7743-7758. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S218944. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31571874 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Preparation and Characterization of Chitosan Nanofiber: Kinetic Studies and Enhancement of Insulin Delivery System.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 May 29;14(11):952. doi: 10.3390/nano14110952. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38869577 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic effect of oral insulin-chitosan nanobeads pectin-dextrin shell on streptozotocin-diabetic male albino rats.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 6;10(15):e35636. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35636. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39170289 Free PMC article.
-
Current Technologies for Managing Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and Their Impact on Quality of Life-A Narrative Review.Life (Basel). 2023 Jul 30;13(8):1663. doi: 10.3390/life13081663. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37629520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of Factors Influencing the Effectiveness of Deformable Nanovesicles for Insulin Nebulization Inhalation.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jun 29;16(7):879. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16070879. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39065576 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Nanomedicine for Precision Insulin Delivery.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jul 15;17(7):945. doi: 10.3390/ph17070945. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065795 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Federation I.D. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 9th ed. International Diabetes Federation; Brussels, Belgium: 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

