Acid Sphingomyelinase Is a Modulator of Contextual Fear
- PMID: 35328819
- PMCID: PMC8954852
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23063398
Acid Sphingomyelinase Is a Modulator of Contextual Fear
Abstract
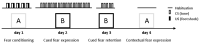
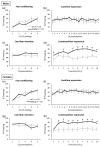
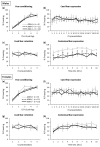
Acid sphingomyelinase (ASM) regulates a variety of physiological processes and plays an important role in emotional behavior. The role of ASM in fear-related behavior has not been investigated so far. Using transgenic mice overexpressing ASM (ASMtg) and ASM deficient mice, we studied whether ASM regulates fear learning and expression of cued and contextual fear in a classical fear conditioning paradigm, a model used to investigate specific attributes of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). We show that ASM does not affect fear learning as both ASMtg and ASM deficient mice display unaltered fear conditioning when compared to wild-type littermates. However, ASM regulates the expression of contextual fear in a sex-specific manner. While ASM overexpression enhances the expression of contextual fear in both male and female mice, ASM deficiency reduces the expression of contextual fear specifically in male mice. The expression of cued fear, however, is not regulated by ASM as ASMtg and ASM deficient mice display similar tone-elicited freezing levels. This study shows that ASM modulates the expression of contextual fear but not of cued fear in a sex-specific manner and adds a novel piece of information regarding the involvement of ASM in hippocampal-dependent aversive memory.
Keywords: ASM; PTSD; contextual fear; cued fear; fear conditioning; fear extinction; fear learning; knock-out mice; transgenic mice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cued and contextual fear conditioning in BTBR mice is improved with training or atomoxetine.Neurosci Lett. 2013 Aug 9;549:120-4. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2013.06.032. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Neurosci Lett. 2013. PMID: 23827222
-
Dorsal hippocampal administration of triiodothyronine enhances long-term memory for trace cued and delay contextual fear conditioning in rats.J Neuroendocrinol. 2006 Nov;18(11):811-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2006.01480.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 2006. PMID: 17026530
-
Deficits in trace cued fear conditioning in galanin-treated rats and galanin-overexpressing transgenic mice.Learn Mem. 2002 Jul-Aug;9(4):178-90. doi: 10.1101/m.49502. Learn Mem. 2002. PMID: 12177231 Free PMC article.
-
Impairments in fear conditioning in mice lacking the nNOS gene.Learn Mem. 2009 May 23;16(6):371-8. doi: 10.1101/lm.1329209. Print 2009 Jun. Learn Mem. 2009. PMID: 19470653 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of CA2 neuronal activity increases behavioral responses to fear conditioning in female mice.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2019 Sep;163:107044. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2019.107044. Epub 2019 Jul 15. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2019. PMID: 31319167 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Brain Region-Specific Expression Levels of Synuclein Genes in an Acid Sphingomyelinase Knockout Mouse Model: Correlation with Depression-/Anxiety-Like Behavior and Locomotor Activity in the Absence of Genotypic Variation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 9;25(16):8685. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168685. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schissel S.L., Jiang X., Tweedie-Hardman J., Jeong T., Camejo E.H., Najib J., Rapp J.H., Williams K.J., Tabas I. Secretory sphingomyelinase, a product of the acid sphingomyelinase gene, can hydrolyze atherogenic lipoproteins at neutral pH. Implications for atherosclerotic lesion development. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:2738–2746. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.5.2738. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

