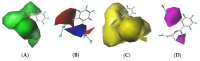PAEs Derivatives' Design for Insulation: Integrated In-Silico Methods, Functional Assessment and Environmentally Friendly Molecular Modification
- PMID: 35328919
- PMCID: PMC8949259
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19063232
PAEs Derivatives' Design for Insulation: Integrated In-Silico Methods, Functional Assessment and Environmentally Friendly Molecular Modification
Abstract
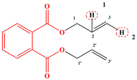
As a common substance in production and life, phthalic acid esters (PAEs), the main component of plastics, have brought more and more serious problems to the environment. This study normalized the insulation, toxicity, and bioconcentration data of 13 PAEs to eliminate the dimensional coefficients of each index, and then used the comprehensive index method to calculate the comprehensive effect value of PAEs with three properties. The comprehensive effect value was used as the data source to construct the 3D-QSAR model of PAE molecular comprehensive effect. The DAP was selected as the target molecule, the distribution of each force field in the three-dimensional equipotential map was analyzed, and 30 molecular modification schemes were created. The constructed single-effect models of insulation, toxicity, and bioconcentration of PAEs and the scoring function module of DS software were used to evaluate the stability and environmental friendliness of PAE derivative molecules. Four PAE derivatives were screened for increased comprehensive effects, enhanced insulation, and reduced toxicity and bioconcentration. By calculating the binding energy of the target molecule and the derivative molecule with the degrading enzyme under different applied electric fields, it was found that the binding energy of DAP-1-NO2-2-CH2C6H5 decreases more than DAP does when there is an applied electric field, indicating that the degradation ability of degrading enzymes on PAE derivative molecules is reduced, which indirectly proves that the insulation is enhanced. The innovation of this paper lies in the insulation, toxicity, and bioenrichment data of PAEs being processed by mathematical method for the first time, and PAEs with high insulation, low toxicity, and low bioconcentration were designed by building a comprehensive model.
Keywords: 3D-QSAR; composite index method; insulation; phthalic acid esters; plasticiser.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy coefficient method assisted quadruple-activities 3D-QSAR pharmacophore model for application in environmentally friendly PAE molecular modification.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Jul;27(19):24103-24114. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-08725-0. Epub 2020 Apr 17. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32301091
-
Enhanced Biodegradation of Phthalic Acid Esters' Derivatives by Plasticizer-Degrading Bacteria (Burkholderia cepacia, Archaeoglobus fulgidus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa) Using a Correction 3D-QSAR Model.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jul 23;17(15):5299. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17155299. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32717867 Free PMC article.
-
Theoretical Design of Biodegradable Phthalic Acid Ester Derivatives in Marine and Freshwater Environments.ChemistryOpen. 2020 Oct 19;9(10):1033-1045. doi: 10.1002/open.202000093. eCollection 2020 Oct. ChemistryOpen. 2020. PMID: 33101830 Free PMC article.
-
[Advances in biodegradation of phthalates esters].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2019 Nov 25;35(11):2104-2120. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.190177. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2019. PMID: 31814358 Review. Chinese.
-
Bacteria-mediated phthalic acid esters degradation and related molecular mechanisms.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Feb;102(3):1085-1096. doi: 10.1007/s00253-017-8687-5. Epub 2017 Dec 14. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29238874 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Design and Mechanism Analysis of Phthalic Acid Ester Substitutes: Improved Biodegradability in Processes of Sewage Treatment and Soil Remediation.Toxics. 2022 Dec 13;10(12):783. doi: 10.3390/toxics10120783. Toxics. 2022. PMID: 36548616 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang T., Hu X.G., Zhou Q.X. The research progress in migration, distribution, biological eddects and analytical methods of microplastics. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2018;63:385–395. doi: 10.1007/s11425-016-0564-5. - DOI
-
- Gorrasi G., Bugatti V., Viscusi G., Vittoria V. Physical and barrier properties of chemically modified pectin with polycaprolactone through an environmentally friendly process. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2021;299:429–437. doi: 10.1007/s00396-020-04699-0. - DOI
-
- Aaliya B., Sunooj K.V., Lackner M. Biopolymer composites: A review. Int. J. Biochem. Plast. 2021;3:40–84. doi: 10.1080/24759651.2021.1881214. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials