Association between the Perceived Household Financial Decline Due to COVID-19 and Smartphone Dependency among Korean Adolescents
- PMID: 35328992
- PMCID: PMC8951075
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19063303
Association between the Perceived Household Financial Decline Due to COVID-19 and Smartphone Dependency among Korean Adolescents
Abstract
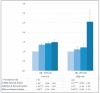
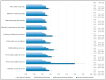
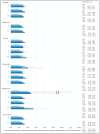
This cross-sectional study identified the association between COVID-19-related perceived household financial decline and smartphone dependency among adolescents in South Korea. Data from the 2020 Youth Risk Behavior Survey of Korea was used and 54,809 middle and high school students were included. COVID-19-related perceived household financial decline was categorized as no financial decline, mild, moderate, and severe. Smartphone dependency was calculated by 10 questions and was largely categorized as yes and no, and as normal, low, and high (prevalence rate: 25.0%). Binary and multinomial regression analyses were performed to analyze the association. The more severe the financial decline, the more pronounced the risk of high-risk smartphone dependency (mild financial decline: odds ratio (OR) 1.11, 95% CI 0.96-1.28; moderate: OR 1.22, 95% CI 1.04-1.43; severe: OR 2.56, 95% CI 2.06-3.17). Poor family relationships (OR 1.06, 95% CI 1.03-1.10) and severe social conflict (OR 2.99, 95% CI 2.50-3.58) were also related to smartphone dependency. The ORs were 2.63 with more than three bathrooms and 1.63 with their own bedroom. Smartphone dependency among adolescents is closely related to COVID-19-related perceived household financial decline. As smartphone dependency relates to complicated psychological issues, further evaluation is necessary, especially for vulnerable adolescents.
Keywords: COVID-19; addictive behavior; adolescent; income; poverty; smartphone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kim Y.H. Volume 18–19 Youone Engineering, Co. Ltd.; Seoul, Korea: 2019. Analysis of cell phone possession and use behavior of children and adolescents. Korea Information Society Development Institute.
-
- Ministry of Science and ICT . The Survey on Smartphone Overdependence. NISA; Scunthorpe, UK: 2021.
-
- Buctot D.B., Kim N., Kim J.J. Factors associated with smartphone addiction prevalence and its predictive capacity for health-related quality of life among Filipino adolescents. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2020;110:104758. doi: 10.1016/j.childyouth.2020.104758. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

