MicroRNA-21 Expression as a Prognostic Biomarker in Oral Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35329083
- PMCID: PMC8948874
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19063396
MicroRNA-21 Expression as a Prognostic Biomarker in Oral Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Oral carcinoma represents one of the main carcinomas of the head and neck region, with a 5-year survival rate of less than 50%. Smoking and tobacco use are recognized risk factors. Prognostic survival biomarkers can be a valid tool for assessing a patient's life expectancy and directing therapy towards specific targets. Among the biomarkers, the alteration of miR-21 expression in tumor tissues is increasingly reported as a valid prognostic biomarker of survival for oral cancer. The purpose of this meta-analysis was, therefore, to investigate and summarize the results in the literature concerning the potential prognostic expression of tissue miR-21 in patients with OSCC.
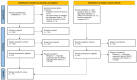
Methods: The systematic review was conducted following the PRISMA guidelines using electronic databases, such as PubMed, Scopus, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, with the use of combinations of keywords, such as miR-21 AND oral cancer, microRNA AND oral cancer, and miR-21. The meta-analysis was performed using the RevMan 5.41 software.
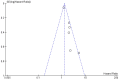
Results: At the end of the article-selection process, 10 studies were included in the meta-analysis, and the result for the main outcome was a pooled HR per overall survival (OS) of 1.29 (1.16-1.44) between high and low expression of miR-21.
Conclusions: The data in the literature and the results emerging from the systematic review indicate that miR-21 can provide a prognostic indication in oral cancer.
Keywords: HNSCC; OSCC; miR-21; microRNA; non-coding RNA; oral cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

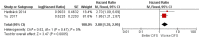


Similar articles
-
The Prognostic Role of miR-31 in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis with Trial Sequential Analysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Apr 27;19(9):5334. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19095334. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35564727 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Electronic cigarettes for smoking cessation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 17;11(11):CD010216. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010216.pub7. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Jan 8;1:CD010216. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010216.pub8. PMID: 36384212 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Does miR-197 Represent a Valid Prognostic Biomarker in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC)? A Systematic Review and Trial Sequential Analysis.J Pers Med. 2022 Aug 31;12(9):1436. doi: 10.3390/jpm12091436. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36143221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of prognostic nutritional index (PNI) in patients with oral cancer: a meta-analysis.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Mar 7;15(5):1615-1627. doi: 10.18632/aging.204576. Epub 2023 Mar 7. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 36897190 Free PMC article.
-
Guided Dental Implant Surgery: Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2023 Feb 13;12(4):1490. doi: 10.3390/jcm12041490. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36836025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression Profile of Circulating Exosomal microRNAs in Leukoplakia, Oral Submucous Fibrosis, and Combined Lesions of Leukoplakia and Oral Submucous Fibrosis.Head Neck Pathol. 2024 Mar 27;18(1):28. doi: 10.1007/s12105-024-01627-4. Head Neck Pathol. 2024. PMID: 38536520 Free PMC article.
-
A PRISMA meta-analysis for diagnostic value of microRNA-21 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma along with bioinformatics research.Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2024 Jun;28(2):739-752. doi: 10.1007/s10006-023-01199-7. Epub 2023 Dec 1. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2024. PMID: 38038839
References
-
- Lissoni A., Agliardi E., Peri A., Marchioni R., Abati S. Oral microbiome and mucosal trauma as risk factors for oral cancer: Beyond alcohol and tobacco. A literature review. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents. 2020;34:11–18. - PubMed

