Cognitive Function among World Trade Center-Exposed Community Members with Mental Health Symptoms
- PMID: 35329128
- PMCID: PMC8948727
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19063440
Cognitive Function among World Trade Center-Exposed Community Members with Mental Health Symptoms
Abstract
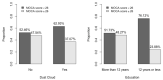
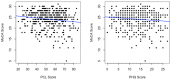
The World Trade Center Environmental Health Center (WTC EHC), is a federally designated clinical center of excellence for surveillance and treatment of WTC disaster exposed community members (WTC Survivors). Cognitive impairment (CI) has been extensively described in WTC responders and a concern for progressive impairment in all WTC disaster exposed groups has been raised. Cognitive status, however, has not been systematically characterized in the WTC Survivor population. We describe cognitive status in a subgroup of the Survivor population referred for mental health evaluation (N = 480) in the WTC EHC as measured by scores on the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) instrument, and examine their association with WTC exposures and individual-level covariates including PTSD and depression screening inventory scores. In regression analyses, probable cognitive impairment (MoCA score < 26) was found in 59% of the study subjects and was significantly associated with age, race/ethnicity, education, income, depression and PTSD scores. Being caught in the dust cloud on 11 September 2011 was significantly associated with cognitive impairment even after controlling for the above. These data suggest an association with cognitive dysfunction in WTC Survivors with exposure to the toxic dust/fumes and psychological stress from the 9/11 terrorist attack and warrant further systematic study.
Keywords: MCI; MoCA; PTSD; World Trade Center; cognition; cognitive impairment; toxin exposure; trauma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Huang C., Kritikos M., Clouston S.A.P., Deri Y., Serrano-Sosa M., Bangiyev L., Santiago-Michels S., Gandy S., Sano M., Bromet E.J., et al. White Matter Connectivity in Incident Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Diffusion Spectrum Imaging Study of World Trade Center Responders at Midlife. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2021;80:1209–1219. doi: 10.3233/JAD-201237. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kritikos M., Clouston S.A.P., Huang C., Pellecchia A.C., Mejia-Santiago S., Carr M.A., Kotov R., Lucchini R.G., Gandy S.E., Bromet E.J., et al. Cortical complexity in world trade center responders with chronic posttraumatic stress disorder. Transl. Psychiatry. 2021;11:597. doi: 10.1038/s41398-021-01719-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clouston S., Pietrzak R.H., Kotov R., Richards M., Spiro A., 3rd, Scott S., Deri Y., Mukherjee S., Stewart C., Bromet E., et al. Traumatic exposures, posttraumatic stress disorder, and cognitive functioning in World Trade Center responders. Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2017;3:593–602. doi: 10.1016/j.trci.2017.09.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clouston S.A., Kotov R., Pietrzak R.H., Luft B.J., Gonzalez A., Richards M., Ruggero C.J., Spiro A., 3rd, Bromet E.J. Cognitive impairment among World Trade Center responders: Long-term implications of re-experiencing the 9/11 terrorist attacks. Alzheimer’s Dement. Diagn. Assess. Dis. Monit. 2016;4:67–75. doi: 10.1016/j.dadm.2016.08.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical