Predicting Adolescent Internet Gaming Addiction from Perceived Discrimination, Deviant Peer Affiliation and Maladaptive Cognitions in the Chinese Population: A Two-Year Longitudinal Study
- PMID: 35329191
- PMCID: PMC8950167
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19063505
Predicting Adolescent Internet Gaming Addiction from Perceived Discrimination, Deviant Peer Affiliation and Maladaptive Cognitions in the Chinese Population: A Two-Year Longitudinal Study
Abstract
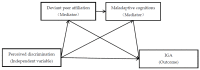
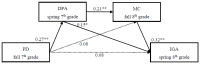
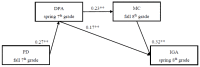
A robust positive association between perceived discrimination and Internet gaming addiction (IGA) among adolescents has been demonstrated by existing research; however, the mediating mechanisms underlying this relationship remain largely unknown. This study, grounded in the cognitive-behavioral and social development models, examined whether deviant peer affiliation and maladaptive cognitions mediated the predictive effect of perceived discrimination on adolescent IGA. Six-hundred-and-sixty students (Meanage = 13.43 years; 367 female participants) recruited from southern China participated in four assessments (fall 7th grade, spring 7th grade, fall 8th grade, spring 8th grade). Participants completed a self-administered questionnaire that assessed their demographics, as well as questionnaire measures of perceived discrimination, deviant peer affiliation, maladaptive cognitions, and IGA. The structural equation model showed that fall 7th grade's perceived discrimination positively predicted spring 7th grade's deviant peer affiliation, which, in turn, increased fall 8th grade's maladaptive cognitions, ultimately increasing spring 8th grade's IGA. Moreover, the indirect effect of fall 7th grade's perceived discrimination on spring 8th grade's IGA via spring 7th grade's deviant peer affiliation was also significant. The results suggested deviant peer affiliation and maladaptive cognitions as potential mediating mechanisms linking perceived discrimination to adolescent IGA. These findings have important implications for the prevention and intervention of adolescent IGA.
Keywords: Internet gaming addiction (IGA); adolescents; deviant peer affiliation; maladaptive cognitions; perceived discrimination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predicting Chinese Adolescent Internet Gaming Addiction From Peer Context and Normative Beliefs About Aggression: A 2-Year Longitudinal Study.Front Psychol. 2018 Jul 6;9:1143. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01143. eCollection 2018. Front Psychol. 2018. PMID: 30034356 Free PMC article.
-
Perceptions of School Climate and Internet Gaming Addiction among Chinese Adolescents: The Mediating Effect of Deviant Peer Affiliation.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Mar 18;19(6):3604. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19063604. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35329291 Free PMC article.
-
Deviant Peer Affiliation as an Explanatory Mechanism in the Association between Corporal Punishment and Physical Aggression: a Longitudinal Study among Chinese Adolescents.J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2017 Nov;45(8):1537-1551. doi: 10.1007/s10802-016-0259-0. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2017. PMID: 28070756
-
A Developmental Perspective on Peer Rejection, Deviant Peer Affiliation, and Conduct Problems Among Youth.Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2015 Dec;46(6):823-38. doi: 10.1007/s10578-014-0522-y. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2015. PMID: 25410430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adolescent peer group identification and characteristics: a review of the literature.Addict Behav. 2007 Aug;32(8):1602-27. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2006.11.018. Epub 2006 Dec 26. Addict Behav. 2007. PMID: 17188815 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Relationship between Medical Students' Perceived Stress and Gaming Behavior at King Saud University.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Dec 1;2022:3220042. doi: 10.1155/2022/3220042. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36506915 Free PMC article.
-
Research on the relationship between gaze anxiety, social media disorder, and perceived discrimination in medical students.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):20562. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05705-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594273 Free PMC article.
-
Zhongyong thinking (doctrine of the mean) and internet addiction: The mediation of maladaptive cognition and the moderation of subject.Front Public Health. 2023 Jan 26;10:1045830. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1045830. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36777778 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal modifiable risk and protective factors of internet gaming disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Behav Addict. 2023 May 24;12(2):375-392. doi: 10.1556/2006.2023.00017. Print 2023 Jun 29. J Behav Addict. 2023. PMID: 37224007 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang X., Huang B., Wong K.M. Prevalence and socio-demographic, anthropometric, and cognitive correlates of internet gaming disorder among children in China. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2021;122:105893. doi: 10.1016/j.childyouth.2020.105893. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

