A Comprehensive Review on the Behaviour of Motorcyclists: Motivations, Issues, Challenges, Substantial Analysis and Recommendations
- PMID: 35329238
- PMCID: PMC8950571
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19063552
A Comprehensive Review on the Behaviour of Motorcyclists: Motivations, Issues, Challenges, Substantial Analysis and Recommendations
Abstract
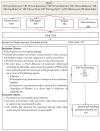
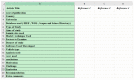
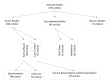
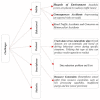
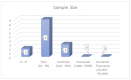
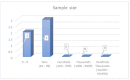
With the continuous emergence of new technologies and the adaptation of smart systems in transportation, motorcyclist driving behaviour plays an important role in the transition towards intelligent transportation systems (ITS). Studying motorcyclist driving behaviour requires accurate models with accurate and complete datasets for better road safety and traffic management. As accuracy is needed in modelling, motorcyclist driving behaviour analyses can be performed using sensors that collect driving behaviour characteristics during real-time experiments. This review article systematically investigates the literature on motorcyclist driving behaviour to present many findings related to the issues, problems, challenges, and research gaps that have existed over the last 10 years (2011-2021). A number of digital databases (i.e., IEEE Xplore®, ScienceDirect, Scopus, and Web of Science) were searched and explored to collect reliable peer-reviewed articles. Out of the 2214 collected articles, only 174 articles formed the final set of articles used in the analysis of the motorcyclist research area. The filtration process consisted of two stages that were implemented on the collected articles. Inclusion criteria were the core of the first stage of the filtration process keeping articles only if they were a study or review written in English or were articles that mainly incorporated the driving style of motorcyclists. The second phase of the filtration process is based on more rules for article inclusion. The criteria of inclusion for the second phase of filtration examined the deployment of motorcyclist driver behaviour characterisation procedures using a real-time-based data acquisition system (DAS) or a questionnaire. The final number of articles was divided into three main groups: reviews (7/174), experimental studies (41/174), and social studies-based articles (126/174). This taxonomy of the literature was developed to group the literature into articles with similar types of experimental conditions. Recommendation topics are also presented to enable and enhance the pace of the development in this research area. Research gaps are presented by implementing a substantial analysis of the previously proposed methodologies. The analysis mainly identified the gaps in the development of data acquisition systems, model accuracy, and data types incorporated in the proposed models. Finally, research directions towards ITS are provided by exploring key topics necessary in the advancement of this research area.
Keywords: driver behaviour; intelligent transportation system; motorcyclists; traffic violation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A systematic review on sensor-based driver behaviour studies: coherent taxonomy, motivations, challenges, recommendations, substantial analysis and future directions.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2021 Aug 25;7:e632. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.632. eCollection 2021. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2021. PMID: 34541305 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
Real-Time Remote Health Monitoring Systems Using Body Sensor Information and Finger Vein Biometric Verification: A Multi-Layer Systematic Review.J Med Syst. 2018 Oct 16;42(12):238. doi: 10.1007/s10916-018-1104-5. J Med Syst. 2018. PMID: 30327939
-
Smart Home-based IoT for Real-time and Secure Remote Health Monitoring of Triage and Priority System using Body Sensors: Multi-driven Systematic Review.J Med Syst. 2019 Jan 15;43(3):42. doi: 10.1007/s10916-019-1158-z. J Med Syst. 2019. PMID: 30648217
-
Understanding the growing role of driving anger in the risk of traffic incidents involving Vietnamese motorcyclists.Traffic Inj Prev. 2022;23(5):215-220. doi: 10.1080/15389588.2022.2056598. Epub 2022 Apr 22. Traffic Inj Prev. 2022. PMID: 35451895
Cited by
-
Modeling Motorcyclists' Aggressive Driving Behavior Using Computational and Statistical Analysis of Real-Time Driving Data to Improve Road Safety and Reduce Accidents.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jun 23;19(13):7704. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19137704. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35805358 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Talal M., Ramli K.N., Zaidan A., Zaidan B., Jumaa F. Review on car-following sensor based and data-generation mapping for safety and traffic management and road map toward ITS. Veh. Commun. 2020;25:100280. doi: 10.1016/j.vehcom.2020.100280. - DOI
-
- Yousif M.T., Sadullah A.F.M., Abu Kassim K.A. A review of behavioural issues contribution to motorcycle safety. IATSS Res. 2020;44:142–154. doi: 10.1016/j.iatssr.2019.12.001. - DOI
-
- Engelbrecht J., Booysen M.J., van Rooyen G.-J., Bruwer F.J. Survey of smartphone-based sensing in vehicles for intelligent transportation system applications. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2015;9:924–935. doi: 10.1049/iet-its.2014.0248. - DOI
-
- Saiprasert C., Thajchayapong S., Pholprasit T., Tanprasert C. Driver behaviour profiling using smartphone sensory data in a V2I environment; Proceedings of the IEEE 2014 International Conference on Connected Vehicles and Expo (ICCVE); Vienna, Austria. 3–7 November 2014; pp. 552–557.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

