Perceptions of School Climate and Internet Gaming Addiction among Chinese Adolescents: The Mediating Effect of Deviant Peer Affiliation
- PMID: 35329291
- PMCID: PMC8954293
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19063604
Perceptions of School Climate and Internet Gaming Addiction among Chinese Adolescents: The Mediating Effect of Deviant Peer Affiliation
Abstract
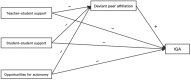
Adolescent internet gaming addiction (IGA) has become a serve public health problem, particularly in China. Despite the fact that the school climate has a significant impact on teenage IGA, little research has looked into the underlying mediating processes. This cross-sectional study looked at the impact of adolescents' perceptions of their school climate (including teacher-student support, student-student support, and opportunities for autonomy) on IGA in a sample of 1053 Chinese adolescents (Meanage = 13.52 years; 52.4% females) using convenient sampling methodology, as well as whether deviant peer affiliation mediated this association. Adolescents' school climate, IGA, and deviant peer affiliation were examined using the School Climate Questionnaire, Internet Gaming Addiction Scale, and two validated tools in this study. The results showed that teacher-student support and student-student support were both negatively associated with IGA, and that these correlations were mediated by deviant peer affiliation. The implications of these findings are discussed.
Keywords: adolescent; deviant peer affiliation; internet gaming addiction (IGA); perceptions of school climate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predicting Adolescent Internet Gaming Addiction from Perceived Discrimination, Deviant Peer Affiliation and Maladaptive Cognitions in the Chinese Population: A Two-Year Longitudinal Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Mar 16;19(6):3505. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19063505. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35329191 Free PMC article.
-
Parental marital conflict and internet gaming disorder among Chinese adolescents: The multiple mediating roles of deviant peer affiliation and teacher-student relationship.PLoS One. 2023 Jan 17;18(1):e0280302. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280302. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36649287 Free PMC article.
-
The Association between Parental Psychological Control, Deviant Peer Affiliation, and Internet Gaming Disorder among Chinese Adolescents: A Two-Year Longitudinal Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Nov 6;17(21):8197. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17218197. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33171961 Free PMC article.
-
Self-Control, Consideration of Future Consequences, and Internet Addiction among Chinese Adolescents: The Moderating Effect of Deviant Peer Affiliation.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Aug 27;18(17):9026. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18179026. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34501614 Free PMC article.
-
Sensation Seeking, Deviant Peer Affiliation, and Internet Gaming Addiction Among Chinese Adolescents: The Moderating Effect of Parental Knowledge.Front Psychol. 2019 Jan 11;9:2727. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02727. eCollection 2018. Front Psychol. 2019. PMID: 30687181 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Psychometric Evaluation of the School Climate and School Identification Measure-Student on Chilean Students: A Bifactor Model Approach.Children (Basel). 2024 Jan 11;11(1):87. doi: 10.3390/children11010087. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38255400 Free PMC article.
-
School Climate and School Identification as Determinants of Internet Gaming Disorder Among Chinese Adolescent Internet Gamers: Cross-Sectional Mediation Study.JMIR Serious Games. 2024 Nov 12;12:e50418. doi: 10.2196/50418. JMIR Serious Games. 2024. PMID: 39622695 Free PMC article.
-
Parental Autonomy Granting, Peer Attachment and Problematic Internet Use Among Chinese Adolescents: The Moderating Effect of School Climate.Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2024 Mar 27. doi: 10.1007/s10578-024-01687-1. Online ahead of print. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2024. PMID: 38536574
-
School resources, self-control and problem behaviors in Chinese adolescents: a longitudinal study in the post-pandemic era.Curr Psychol. 2022 Dec 29:1-13. doi: 10.1007/s12144-022-04178-5. Online ahead of print. Curr Psychol. 2022. PMID: 36593906 Free PMC article.
-
Problematic Smartphone Use Leads to Behavioral and Cognitive Self-Control Deficits.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jun 17;19(12):7445. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19127445. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35742695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Young K.S. When Gaming Becomes an Obsession: Help for Parents and Their Children to Treat Online Gaming Addiction. Center for Internet Addiction, 2010. [(accessed on 19 December 2021)]. Available online: www.netaddiction.com.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous