HBM4EU Chromates Study: Determinants of Exposure to Hexavalent Chromium in Plating, Welding and Other Occupational Settings
- PMID: 35329370
- PMCID: PMC8953290
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19063683
HBM4EU Chromates Study: Determinants of Exposure to Hexavalent Chromium in Plating, Welding and Other Occupational Settings
Abstract
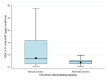
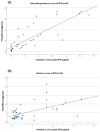
Work-related exposures in industrial processing of chromate (chrome plating, surface treatment and welding) raise concern regarding the health risk of hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)). In this study, performed under the HBM4EU project, we focused on better understanding the determinants of exposure and recognising how risk management measures (RMMs) contribute to a reduction in exposure. HBM and occupational hygiene data were collected from 399 workers and 203 controls recruited in nine European countries. Urinary total chromium (U-Cr), personal inhalable and respirable dust of Cr and Cr(VI) and Cr from hand wipes were collected. Data on the RMMs were collected by questionnaires. We studied the association between different exposure parameters and the use of RMMs. The relationship between exposure by inhalation and U-Cr in different worker groups was analysed using regression analysis and found a strong association. Automatisation of Cr electroplating dipping explained lower exposure levels in platers. The use of personal protective equipment resulted in lower U-Cr levels in welding, bath plating and painting. An effect of wearing gloves was observed in machining. An effect of local exhaust ventilation and training was observed in welding. Regression analyses showed that in platers, exposure to air level of 5 µg/m3 corresponds to U-Cr level of 7 µg/g creatinine. In welders, the same inhalation exposure resulted in lower U-Cr levels reflecting toxicokinetic differences of different chromium species.
Keywords: air monitoring; biomonitoring; dermal exposure; exposure determinants; hexavalent chromium; occupational hygiene; risk management measures.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The contents, including any opinions and/or conclusions expressed of this manuscript, are those of the authors alone and do not necessarily reflect the opinions or policy of the organizations to which they are employed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HBM4EU chromates study - Overall results and recommendations for the biomonitoring of occupational exposure to hexavalent chromium.Environ Res. 2022 Mar;204(Pt A):111984. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.111984. Epub 2021 Sep 4. Environ Res. 2022. PMID: 34492275
-
The SAM-Krom biomonitoring study shows occupational exposure to hexavalent chromium and increased genotoxicity in Denmark.Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2025 Mar;264:114444. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2024.114444. Epub 2024 Sep 23. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2025. PMID: 39317609
-
HBM4EU chromates study - Usefulness of measurement of blood chromium levels in the assessment of occupational Cr(VI) exposure.Environ Res. 2022 Nov;214(Pt 1):113758. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.113758. Epub 2022 Jun 25. Environ Res. 2022. PMID: 35764127
-
The HBM4EU chromates study - Outcomes and impacts on EU policies and occupational health practices.Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2023 Mar;248:114099. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2022.114099. Epub 2022 Dec 17. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2023. PMID: 36528954 Review.
-
Cancer Risks of Hexavalent Chromium in the Respiratory Tract.J UOEH. 2018;40(2):157-172. doi: 10.7888/juoeh.40.157. J UOEH. 2018. PMID: 29925735 Review.
Cited by
-
Occupational Exposure to Hexavalent Chromium, Nickel and PAHs: A Mixtures Risk Assessment Approach Based on Literature Exposure Data from European Countries.Toxics. 2022 Jul 29;10(8):431. doi: 10.3390/toxics10080431. Toxics. 2022. PMID: 36006111 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Dose Hexavalent Chromium Exposure Induces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Apoptosis in Rat Liver.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024 Sep;202(9):4136-4145. doi: 10.1007/s12011-023-03995-4. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024. PMID: 38064039
-
HBM4EU chromates study - the measurement of hexavalent and trivalent chromium in exhaled breath condensate samples from occupationally exposed workers across Europe.Toxicol Lett. 2023 Feb 15;375:59-68. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2022.12.009. Epub 2022 Dec 16. Toxicol Lett. 2023. PMID: 36535516 Free PMC article.
-
HBM4EU Chromates Study-Genotoxicity and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Workers Exposed to Hexavalent Chromium.Toxics. 2022 Aug 18;10(8):483. doi: 10.3390/toxics10080483. Toxics. 2022. PMID: 36006162 Free PMC article.
-
Metals (Cr, Mn, Co, Ni) concentration in the blood plasma and urine od Polish welders and telomere length as an potential indicator of toxicity of metals welding fumes exposure.Int J Occup Med Environ Health. 2025 Mar 11;38(1):70-90. doi: 10.13075/ijomeh.1896.02493. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Int J Occup Med Environ Health. 2025. PMID: 40008862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- NIOSH . Occupational Exposure to Hexavalent Chromium. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health; Washington, DC, USA: 2013. [(accessed on 11 February 2022)]. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/docs/2013128/pdfs/2013_128.pdf?id=0.26616/NIOS....
-
- Viegas S., Jeddi M.Z., Hopf N.B., Bessems J., Palmen N., Galea K., Jones K., Kujath P., Duca R.C., Verhagen H., et al. Biomonitoring as an underused exposure assessment tool in Occupational Safety and Health context–Challenges and way forward! Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2020;17:5884. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17165884. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Saha R., Nandi R., Saha B. Sources and toxicity of hexavalent chromium. J. Coord. Chem. 2011;64:1782–1806. doi: 10.1080/00958972.2011.583646. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

