Current Research and Challenges in Bitumen Emulsion Manufacturing and Its Properties
- PMID: 35329476
- PMCID: PMC8952829
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15062026
Current Research and Challenges in Bitumen Emulsion Manufacturing and Its Properties
Abstract
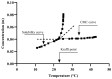
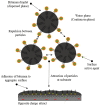
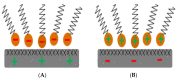
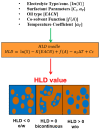
The global increase of road infrastructure and its impact on the environment requires serious attention to develop sustainable and environmentally friendly road materials. One group of those materials is produced by using bitumen emulsion. However, there are still scientific and technical obstacles standing against its regular application. The bitumen emulsion formulation process and compositional optimization are subjected to a high number of degrees of freedom. Consequently, obtaining the desired product is mostly based on a series of random and tedious trials because of the enormous number of tests that are carried out to meet the required properties, such as emulsion stability, viscosity, droplet size (and distribution), and bitumen emulsion chemistry. Several pre-established formulation procedures have been presented in the literature. Some of them have technical limitations to be utilized for practical industrial application, whereas others are still not understood enough to be applied in bitumen emulsion formulation. Therefore, discussing some important issues in this field could be useful to offer a practical guide for bitumen emulsion manufacturers when trying to formulate a well-defined bitumen emulsion to best fit its use in pavement infrastructure rather than to simply to meet standard specifications. This review paper aims to enable the ultimate potential of bitumen emulsion by further reviewing the research progress of bitumen emulsion manufacturing and discussing the literature available up to now on this topic, in the realm of bitumen emulsion manufacturing and emulsion chemistry.
Keywords: bitumen emulsion; emulsification temperature; formulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures











Similar articles
-
Study of the Incorporation of Ladle Furnace Slag in the Manufacture of Cold In-Place Recycling with Bitumen Emulsion.Materials (Basel). 2020 Oct 26;13(21):4765. doi: 10.3390/ma13214765. Materials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33114516 Free PMC article.
-
Study of the Stiffness of the Bitumen Emulsion Based Cold Recycling Mixes for Road Base Courses.Materials (Basel). 2020 Dec 1;13(23):5473. doi: 10.3390/ma13235473. Materials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33271782 Free PMC article.
-
Studies of the microstructure of polymer-modified bitumen emulsions using confocal laser scanning microscopy.J Microsc. 2001 Dec;204(Pt 3):252-7. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2818.2001.00955.x. J Microsc. 2001. PMID: 11903802
-
Durability of bitumen binder reinforced with polymer additives: Towards upgrading Nigerian local bitumen.Heliyon. 2024 May 8;10(10):e30825. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30825. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38778993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bitumen Aging-Laboratory Simulation Methods Used in Practice and Selected Directions of Research on New Methods.Materials (Basel). 2023 Jan 16;16(2):853. doi: 10.3390/ma16020853. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36676590 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Performance and Morphology of Waterborne Polyurethane Asphalt in the Vicinity of Phase Inversion.Materials (Basel). 2024 Jul 8;17(13):3368. doi: 10.3390/ma17133368. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38998448 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nikolaides A.F. Bituminous Mixtures & Pavements VI. CRC Press; London, UK: 2015. - DOI
-
- Autelitano F., Giuliani F. Analytical assessment of asphalt odor patterns in hot mix asphalt production. J. Clean. Prod. 2018;172:1212–1223. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.248. - DOI
-
- Gorman J.L., Crawford R.J., Harding I.H. Bitumen emulsions in road construction—A review. Road Transp. Res. 2004;13:25.
-
- Read J., Whiteoak D. The Shell Bitumen Handbook. Thomas Telford; London, UK: 2003. - DOI
-
- James A. Asphalt Emulsion Technology. Transportation Research Board; Washington, DC, USA: 2006. Overview of asphalt emulsion; pp. 1–15.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

