Study of Nano h-BN Impact on Lubricating Properties of Selected Oil Mixtures
- PMID: 35329507
- PMCID: PMC8953908
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15062052
Study of Nano h-BN Impact on Lubricating Properties of Selected Oil Mixtures
Abstract
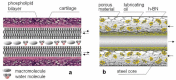
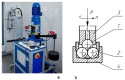
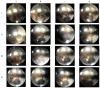
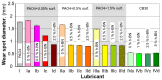
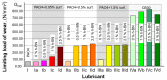
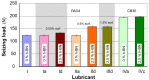
Our experiments aimed to study the influence of layered materials with nanometric-scale particles, which are part of lubricant oils, on their tribological properties. The object of this study was a lubricant oil made using base oil PAO4, which contained nanoparticle hexagonal boron nitride (nano h-BN) and a dispersant based on succinic acid imide. Comparative tests for engine oil (CB30) were also performed. The paper presents the method of preparing the test material and the tribological test results, including wear spot diameter (wear mark), limit wear load, and seizure load. The test results obtained demonstrate that nano-hexagonal boron nitride improves the tribological properties of lubricant oils. However, oil preparation and the quantitative selection of components markedly influence the results.
Keywords: CB30; PAO4; friction; hexagonal boron nitride; lubricity; nanomaterials.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on the tribological properties of lubricating oil: an experimental investigation.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 25;12(1):5201. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-09245-2. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35338221 Free PMC article.
-
Research on the Influence of the Manufacturing Process Conditions of Iron Sintered with the Addition of Layered Lubricating Materials on its Selected Properties.Materials (Basel). 2020 Oct 26;13(21):4782. doi: 10.3390/ma13214782. Materials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33114750 Free PMC article.
-
Performance evaluation of nano-graphene lubricating oil with high dispersion and low viscosity used in diesel engines.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 16;19(8):e0307394. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307394. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39150954 Free PMC article.
-
Ti3C2TXderived layered MXenes as friction and wear reducing additives in lubricating oils: a detailed review.Nanotechnology. 2025 Mar 20;36(17). doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/adbb73. Nanotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40020246 Review.
-
Review of two-dimensional nanomaterials in tribology: Recent developments, challenges and prospects.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2023 Nov;321:103004. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2023.103004. Epub 2023 Sep 30. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2023. PMID: 37837702 Review.
References
-
- Archard J.E. Contact and rubbing of flat surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 1953;24:981. doi: 10.1063/1.1721448. - DOI
-
- Bayer R.G., Clinton W.C., Nelson C.W., Schumacher R.A. Engineering model for wear. Wear. 1962;5:378–391. doi: 10.1016/0043-1648(62)90075-3. - DOI
-
- Zum Gahr K.H., editor. Microstructure and Wear of Materials. Elsevier B.V.; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 1987. - DOI
-
- Kuczmaszewski J. Fundamentals of Metal-Metal Adhesive Joint Design. Lublin University of Technology; Lublin, Poland: 2006.
-
- Kałdoński T. Podstawowe Problemy Analizowania Procesów Tribologicznych (Basic Problems of Analyzing Tribological Processes) WAT; Warszawa, Poland: 2015.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

