Characterization of Hydroxyapatite Film Obtained by Er:YAG Pulsed Laser Deposition on Sandblasted Titanium: An In Vitro Study
- PMID: 35329758
- PMCID: PMC8955651
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15062306
Characterization of Hydroxyapatite Film Obtained by Er:YAG Pulsed Laser Deposition on Sandblasted Titanium: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
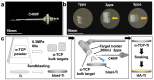
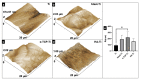
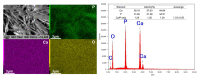
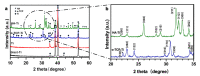
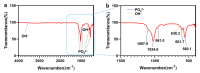
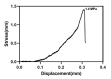
The surface of titanium (Ti) dental implants must be modified to improve their applicability, owing to the biological inertness of Ti. This study aims to use sandblasting as a pretreatment method and prepare a hydroxyapatite (HA) coating on Ti to improve its biocompatibility and induce bone bonding and osteogenesis. In this paper, sandblasted Ti discs were coated with α-tricalcium phosphate (α-TCP) via Er:YAG pulsed laser deposition (Er:YAG-PLD). An HA coating was then obtained via the hydrothermal treatment of the discs at 90 °C for 10 h. The surface characteristics of the samples were evaluated by SEM, SPM, XPS, XRD, FTIR, and tensile tests. Rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells were seeded on the HA-coated discs to determine cellular responses in vitro. The surface characterization results indicated the successful transformation of the HA coating with a nanorod-like morphology, and its surface roughness increased. In vitro experiments revealed increased cell attachment on the HA-coated discs, as did the cell morphology of fluorescence staining and SEM analysis; in contrast, there was no increase in cell proliferation. This study confirms that Er:YAG-PLD could be used as an implant surface-modification technique to prepare HA coatings with a nanorod-like morphology on Ti discs.
Keywords: Er:YAG laser; hydroxyapatite coating; pulsed laser deposition; titanium implant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Effect of Er:YAG Pulsed Laser-Deposited Hydroxyapatite Film on Titanium Implants on M2 Macrophage Polarization In Vitro and Osteogenesis In Vivo.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 26;25(1):349. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010349. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203519 Free PMC article.
-
Biocompatibility of dental implants coated with hydroxyapatite using pulsed Er:YAG laser deposition.Dent Mater J. 2024 Mar 29;43(2):269-275. doi: 10.4012/dmj.2023-235. Epub 2024 Feb 29. Dent Mater J. 2024. PMID: 38417859
-
Hydroxyapatite Film Coating by Er:YAG Pulsed Laser Deposition Method for the Repair of Enamel Defects.Materials (Basel). 2021 Dec 6;14(23):7475. doi: 10.3390/ma14237475. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34885628 Free PMC article.
-
Implant surface modification using laser guided coatings: in vitro comparison of mechanical properties.J Prosthodont. 2008 Jul;17(5):357-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-849X.2008.00307.x. Epub 2008 Jun 9. J Prosthodont. 2008. PMID: 18544138
-
Ion-substituted calcium phosphate coatings by physical vapor deposition magnetron sputtering for biomedical applications: A review.Acta Biomater. 2019 Apr 15;89:14-32. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.03.006. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 30851454 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Broad Spectrum of Titanium-Niobium Implants and Hydroxyapatite Coatings-A Review.Materials (Basel). 2024 Dec 19;17(24):6206. doi: 10.3390/ma17246206. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39769805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Er:YAG Pulsed Laser-Deposited Hydroxyapatite Film on Titanium Implants on M2 Macrophage Polarization In Vitro and Osteogenesis In Vivo.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 26;25(1):349. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010349. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203519 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Hydroxyapatite Coating by Er: YAG Pulsed Laser Deposition on the Bone Formation Efficacy by Polycaprolactone Porous Scaffold.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 12;23(16):9048. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169048. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012313 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ottria L., Lauritano D., Andreasi Bassi M., Palmieri A., Candotto V., Tagliabue A., Tettamanti L. Mechanical, Chemical and Biological Aspects of Titanium and Titanium Alloys in Implant Dentistry. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents. 2018;32:81–90. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

