Double Balloon Catheter (Plus Oxytocin) versus Dinoprostone Vaginal Insert for Term Rupture of Membranes: A Randomized Controlled Trial (RUBAPRO)
- PMID: 35329852
- PMCID: PMC8952372
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11061525
Double Balloon Catheter (Plus Oxytocin) versus Dinoprostone Vaginal Insert for Term Rupture of Membranes: A Randomized Controlled Trial (RUBAPRO)
Abstract
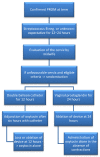
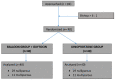
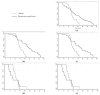
Background: The aim of this study is to demonstrate that a double balloon catheter combined with oxytocin decreases time between induction of labor and delivery (TID) as compared to a vaginal dinoprostone insert in cases of premature rupture of membranes at term. Methods: This is a prospective, randomized, controlled trial including patient undergoing labor induction for PROM at term with an unfavorable cervix in Clermont-Ferrand university hospital. We compared the double balloon catheter over a period of 12 h with adjunction of oxytocin 6 h after catheter insertion versus dinoprostone vaginal insert. After device ablation, cervical ripening continued only with oxytocin. The main outcome was TID. Secondary outcomes concerned delivery mode, as well as maternal and fetal outcome, and were adjusted for parity. Results: 40 patients per group were randomized. Each group had similar baseline characteristics. The study failed to demonstrate reduced TID (16.2 versus 20.2 h, ES = 0.16 (−0.27 to 0.60), p = 0.12) in the catheter group versus dinoprostone except in nulliparous women (17.0 versus 26.5 h, ES = 0.62 (0.10 to 1.14), p = 0.006). The rate of vaginal delivery <24 h significantly increased with combined induction (88.5% versus 66.6%, p = 0.03). No statistical difference was observed concerning caesarean rate (12.5% versus 17.5%, p > 0.05), chorioamnionitis (0% versus 2.5%, p = 1), postpartum endometritis, or maternal or neonatal outcomes. Procedure-related pain and tolerance to devices were found to be similar for the two methods. Interpretation: The double balloon catheter combined with oxytocin is an alternative for cervical ripening in case of PROM at term, and may reduce TID in nulliparous women.
Keywords: cervical ripening balloon; labor induction; nulliparous; premature rupture of membranes; unfavorable cervix.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Induction of labour in case of premature rupture of membranes at term with an unfavourable cervix: protocol for a randomised controlled trial comparing double balloon catheter (+oxytocin) and vaginal prostaglandin (RUBAPRO) treatments.BMJ Open. 2019 Jun 20;9(6):e026090. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-026090. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31227530 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the effectiveness and safety of Dinoprostone vaginal insert and double-balloon catheter as cervical ripening treatments in Chinese patients.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 9;9:976983. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.976983. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36160157 Free PMC article.
-
Double-balloon catheter vs. dinoprostone vaginal insert for induction of labor with an unfavorable cervix.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2015 Jun;291(6):1221-7. doi: 10.1007/s00404-014-3547-3. Epub 2014 Nov 19. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2015. PMID: 25408273 Clinical Trial.
-
Double-balloon catheter versus dinoprostone insert for labour induction: a meta-analysis.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2019 Jan;299(1):7-12. doi: 10.1007/s00404-018-4929-8. Epub 2018 Oct 12. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2019. PMID: 30315411 Review.
-
Double balloon catheter for induction of labour in Chinese women with previous caesarean section: one-year experience and literature review.Hong Kong Med J. 2015 Jun;21(3):243-50. doi: 10.12809/hkmj144404. Epub 2015 May 22. Hong Kong Med J. 2015. PMID: 25999032 Review.
Cited by
-
A model to predict delivery time following induction of labor at term with a dinoprostone vaginal insert: a retrospective study.Ir J Med Sci. 2024 Jun;193(3):1343-1350. doi: 10.1007/s11845-023-03568-3. Epub 2023 Nov 10. Ir J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 37947994 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Senat M.-V., Schmitz T., Bouchghoul H., Diguisto C., Girault A., Paysant S., Sibiude J., Lassel L., Sentilhes L. Term Prelabor Rupture of Membranes: CNGOF Guidelines for Clinical Practice—Short Text. Gynecol. Obstet. Fertil. Senol. 2020;48:15–18. - PubMed
-
- Seaward P.G., Hannah M.E., Myhr T.L., Farine D., Ohlsson A., Wang E.E., Haque K., Weston J.A., Hewson S.A., Ohel G., et al. International multicentre term prelabor rupture of membranes study: Evaluation of predictors of clinical chorioamnionitis and postpartum fever in patients with prelabor rupture of membranes at term. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1997;177:1024–1029. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9378(97)70007-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Huret C., Pereira B., Collange V., Delabaere A., Rouzaire M., Lemery D., Sapin V., Gallot D. Premature rupture of membranes≥37 weeks of gestation: Predictive factors for labour onset within 24 hours. Gynecol. Obstet. Fertil. Senol. 2017;45:348–352. - PubMed
-
- Sibiude J. Term Prelabor Rupture of Membranes: CNGOF Guidelines for Clinical Practice—Timing of Labor Induction. Gynecol. Obstet. Fertil. Senol. 2020;48:35–47. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

