Effects of Iloprost on Oxygenation during One-Lung Ventilation in Patients with Low Diffusing Capacity for Carbon Monoxide: A Randomized Controlled Study
- PMID: 35329869
- PMCID: PMC8949409
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11061542
Effects of Iloprost on Oxygenation during One-Lung Ventilation in Patients with Low Diffusing Capacity for Carbon Monoxide: A Randomized Controlled Study
Abstract
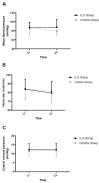
The protective mechanism of hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction during one-lung ventilation (OLV) is impaired in patients with a low diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO). We hypothesized that iloprost inhalation would improve oxygenation and lung mechanics in patients with low DLCO who underwent pulmonary resection. Forty patients with a DLCO < 75% were enrolled. Patients were allocated into either an iloprost group (ILO group) or a control group (n = 20 each), in which iloprost and saline were inhaled, respectively. The partial pressure of arterial oxygen/fraction of inspired oxygen (PaO2/FiO2) ratio, pulmonary shunt fraction, alveolar dead space, dynamic compliance, and hemodynamic parameters were assessed 20 min after the initiation of OLV and 20 min after drug administration. Repeated variables were analyzed using a linear mixed model between the groups. Data from 39 patients were analyzed. After iloprost inhalation, the ILO group exhibited a significant increase in the PaO2/FiO2 ratio and a decrease in alveolar dead space compared with the control group (p = 0.025 and p = 0.042, respectively). Pulmonary shunt, dynamic compliance, hemodynamic parameters, and short-term prognosis were comparable between the two groups. Selective iloprost administration during OLV reduced alveolar dead space and improved oxygenation while minimally affecting hemodynamics and short-term prognosis.
Keywords: diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide; iloprost; one-lung ventilation; oxygenation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Iloprost on Arterial Oxygenation and Lung Mechanics during One-Lung Ventilation in Supine-Positioned Patients: A Randomized Controlled Study.J Pers Med. 2022 Jun 27;12(7):1054. doi: 10.3390/jpm12071054. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35887551 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Inhaled Iloprost on Lung Mechanics and Myocardial Function During One-Lung Ventilation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients Combined With Poor Lung Oxygenation.Anesth Analg. 2020 May;130(5):1407-1414. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000004733. Anesth Analg. 2020. PMID: 32167976 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of a 1:1 inspiratory to expiratory ratio on respiratory mechanics and oxygenation during one-lung ventilation in patients with low diffusion capacity of lung for carbon monoxide: a crossover study.J Clin Anesth. 2015 Sep;27(6):445-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2015.06.012. Epub 2015 Aug 9. J Clin Anesth. 2015. PMID: 26263797 Clinical Trial.
-
The Effects of Iloprost on Oxygenation During One-Lung Ventilation for Lung Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Clin Med. 2019 Jul 5;8(7):982. doi: 10.3390/jcm8070982. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31284472 Free PMC article.
-
A randomized controlled trial of positive end-expiratory pressure on pulmonary oxygenation and biventricular function in esophageal cancer patients receiving one-lung ventilation under a lower FiO2.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022 Oct;13(5):2105-2114. doi: 10.21037/jgo-22-522. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36388664 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparison between Sugammadex and Neostigmine after Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery-Thymectomy in Patients with Myasthenia Gravis: A Single-Center Retrospective Exploratory Analysis.J Pers Med. 2023 Sep 15;13(9):1380. doi: 10.3390/jpm13091380. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37763148 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Iloprost on Arterial Oxygenation and Lung Mechanics during One-Lung Ventilation in Supine-Positioned Patients: A Randomized Controlled Study.J Pers Med. 2022 Jun 27;12(7):1054. doi: 10.3390/jpm12071054. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35887551 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

