Outcomes of COVID-19 Critically Ill Extremely Elderly Patients: Analysis of a Large, National, Observational Cohort
- PMID: 35329870
- PMCID: PMC8951481
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11061544
Outcomes of COVID-19 Critically Ill Extremely Elderly Patients: Analysis of a Large, National, Observational Cohort
Abstract
Background: During the COVID-19 pandemic, resource allocation became a major problem in globally overwhelmed ICUs. The main goal of this study was to describe the clinical characteristics of the very elderly patients (aged ≥ 80 years) with COVID-19 admitted in Romanian ICUs. The study objectives were to evaluate and determine the factors associated with ICU mortality.
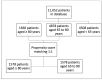
Methods: We designed a national, multicentric, observational platform with prospective enrolment. This study included patients aged ≥ 80 years admitted in Romanian ICUs with SARS-CoV-2 infection from March 2020 to December 2021.
Results: We included 1666 patients with a median age of 83 years and 78% ICU mortality. Male sex, dyspnoea, lower Glasgow Coma Scale and lower SpO2 at ICU admission, the need for mechanical ventilation (MV), and corticosteroid use were independently associated with mortality. A total of 886/1666 (53%) elderly patients underwent invasive mechanical ventilation, with a mortality of 97%. The age impact on mortality was confirmed by a 1:1 propensity matching with less elderly ICU patients.
Conclusion: In extremely elderly patients with COVID-19 admitted in the ICU, mortality is high, particularly when requiring MV. Therapy should be directed towards the optimization of less invasive ventilatory methods and the use of MV and corticosteroids only in highly selected patients.
Keywords: COVID-19; ICU; elderly; mechanical ventilation; mortality; outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Similar articles
-
Mechanical ventilation and mortality among 223 critically ill patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A multicentric study in Germany.Aust Crit Care. 2021 Mar;34(2):167-175. doi: 10.1016/j.aucc.2020.10.009. Epub 2020 Oct 27. Aust Crit Care. 2021. PMID: 33250401 Free PMC article.
-
Baseline Characteristics and Outcomes of 1591 Patients Infected With SARS-CoV-2 Admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy.JAMA. 2020 Apr 28;323(16):1574-1581. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.5394. JAMA. 2020. PMID: 32250385 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Factors Associated With Mortality Among Patients With COVID-19 in Intensive Care Units in Lombardy, Italy.JAMA Intern Med. 2020 Oct 1;180(10):1345-1355. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3539. JAMA Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32667669 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characteristics and day-90 outcomes of 4244 critically ill adults with COVID-19: a prospective cohort study.Intensive Care Med. 2021 Jan;47(1):60-73. doi: 10.1007/s00134-020-06294-x. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Intensive Care Med. 2021. PMID: 33211135 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with COVID-19 infection: a systematic review.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021 Jan;27(1):47-54. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.10.017. Epub 2020 Oct 23. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021. PMID: 33190794 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Development and Internal Validation of a New Prognostic Model Powered to Predict 28-Day All-Cause Mortality in ICU COVID-19 Patients-The COVID-SOFA Score.J Clin Med. 2022 Jul 18;11(14):4160. doi: 10.3390/jcm11144160. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35887924 Free PMC article.
-
The COVID-19 Vaccination Coverage in ICU Patients with Severe COVID-19 Infection in a Country with Low Vaccination Coverage-A National Retrospective Analysis.J Clin Med. 2023 Feb 22;12(5):1749. doi: 10.3390/jcm12051749. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36902535 Free PMC article.
-
Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19 - From Pathophysiological Mechanisms to a Personalized Therapeutic Model.J Crit Care Med (Targu Mures). 2023 Jul 31;9(3):148-161. doi: 10.2478/jccm-2023-0023. eCollection 2023 Jul. J Crit Care Med (Targu Mures). 2023. PMID: 37588184 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Demiselle J., Duval G., Hamel J.-F., Renault A., Bodet-Contentin L., Martin-Lefèvre L., Vivier D., Villers D., Lefèvre M., Robert R., et al. Determinants of hospital and one-year mortality among older patients admitted to intensive care units: Results from the multicentric SENIOREA cohort. Ann. Intensive Care. 2021;11:35. doi: 10.1186/s13613-021-00804-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous