Prognostic Value of Non-Invasive Global Myocardial Work in Asymptomatic Aortic Stenosis
- PMID: 35329881
- PMCID: PMC8953091
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11061555
Prognostic Value of Non-Invasive Global Myocardial Work in Asymptomatic Aortic Stenosis
Abstract
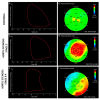
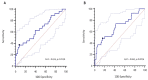
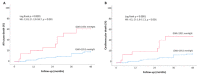
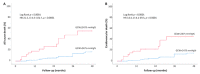
This study aimed to evaluate the modification of non-invasive myocardial work (MW) indices related to aortic stenosis (AS) stages of cardiac damage and their prognostic value. The echocardiographic and outcome data of 170 patients, with asymptomatic moderate-to-severe AS and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) ≥ 50%, and 50 age- and sex-comparable healthy controls were analysed. Primary endpoints were the occurrence of all-cause and cardiovascular death. Increased values of the global work index (GWI), global constructive work (GCW), and global wasted work (GWW) were observed in AS patients compared to controls (GWI: 2528 ± 521 vs. 2005 ± 302 mmHg%, GCW: 2948 ± 598 vs. 2360 ± 353 mmHg%, p < 0.001; GWW: 139 ± 90 vs. 90 ± 49 mmHg%, p = 0.005), with no changes in the global work efficiency. When patients were stratified according to the stages of cardiac damage, the GWI showed lower values in Stage 3−4 as compared to Stage 0 and Stage 2 (p = 0.024). During a mean follow-up of 30 months, 27 patients died. In multivariable Cox-regression analysis, adjusted for confounders, GWI (HR: 0.998, CI: 0.997−1.000; p = 0.034) and GCW (HR:0.998, CI: 0.997−0.999; p = 0.003) were significantly associated with excess mortality. When used as categorical variables, a GWI ≤ 1951 mmHg% and a GCW ≤ 2475 mmHg% accurately predicted all-cause and cardiovascular death at 4-year follow-up. In conclusion, in asymptomatic patients with moderate-to-severe AS, reduced values of GWI and GCW are associated with increased mortality. Therefore, the evaluation of MW indices may allow for a better identification of asymptomatic patients with moderate to severe AS and preserved LVEF whom are at increased risk of worse prognosis during follow-up.
Keywords: aortic stenosis; asymptomatic; cardiac damage; myocardial work; prognosis; staging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of left ventricular myocardial work indices in patients with severe aortic stenosis undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023 Nov 23;24(12):1682-1689. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jead157. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37409583 Free PMC article.
-
[The value of myocardial work in detecting the reduction of left ventricular global systolic function in acute myocardial infarction patients with preserved ejection fraction].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2022 Feb 24;50(2):160-165. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112148-20211027-00921. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35172461 Chinese.
-
Usefulness of Echocardiographic Parameters of Myocardial Work in Patients with Aortic Stenosis Undergoing Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation.J Clin Med. 2025 Jan 15;14(2):512. doi: 10.3390/jcm14020512. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 39860518 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing Myocardial Strain and Myocardial Work as a Marker for Hypertensive Heart Disease: A Meta-Analysis.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Jul 31;24(8):217. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2408217. eCollection 2023 Aug. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 39076705 Free PMC article.
-
Echocardiography myocardial work assessment of chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Med Ultrason. 2025 Mar 24. doi: 10.11152/mu-4502. Online ahead of print. Med Ultrason. 2025. PMID: 40146979 Review.
Cited by
-
Towards non-invasive assessment of myocardial work using myocardial stiffness and strain: a human pilot study.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2025 May 30;26(6):1051-1064. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jeaf089. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40085822
-
Prognostic Relevance of Global Myocardial Work Index in Patients with Moderate Aortic Valve Stenosis.J Clin Med. 2023 Dec 14;12(24):7694. doi: 10.3390/jcm12247694. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38137763 Free PMC article.
-
Echocardiographic Evaluation after Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation: A Comprehensive Review.Life (Basel). 2023 Apr 24;13(5):1079. doi: 10.3390/life13051079. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37240724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Echocardiographic Evaluation of Aortic Stenosis: A Comprehensive Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jul 29;13(15):2527. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13152527. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37568890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic value of left ventricular myocardial work indices in patients with severe aortic stenosis undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023 Nov 23;24(12):1682-1689. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jead157. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37409583 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vahanian A., Beyersdorf F., Praz F., Milojevic M., Baldus S., Bauersachs J., Capodanno D., Conradi L., De Bonis M., De Paulis R., et al. 2021 ESC/EACTS Guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease. Eur. Heart J. 2021;43:ehab395. - PubMed
-
- Lancellotti P., Magne J., Dulgheru R., Clavel M.A., Donal E., Vannan M.A., Chambers J., Rosenhek R., Habib G., Lloyd G., et al. Outcomes of Patients with Asymptomatic Aortic Stenosis Followed up in Heart Valve Clinics. JAMA Cardiol. 2018;3:1060–1068. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2018.3152. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

