A Three-Protein Panel to Support the Diagnosis of Sepsis in Children
- PMID: 35329889
- PMCID: PMC8955185
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11061563
A Three-Protein Panel to Support the Diagnosis of Sepsis in Children
Abstract
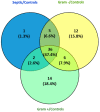
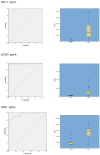
Sepsis is a syndrome without a standard validated diagnostic test. Early recognition is crucial. Serum proteome analysis in children with sepsis may identify new biomarkers. This study aimed to find suitable blood biomarkers for an early diagnosis of sepsis. An analytical observational case-control study was carried out in a single center. Children admitted to a Pediatric Intensive Care Unit with clinical diagnosed sepsis were eligible for study. A proteomic analysis conducted by mass spectrometry was performed. Forty patients with sepsis and 24 healthy donors were recruited. Proteomics results revealed 44 proteins differentially expressed between patients and healthy controls. Six proteins were selected to be validated: lactoferrin, serum amyloid-A1 (SAA-1), complement factor B, leucine-rich alpha-2 glycoprotein (LRG1), soluble interleukin-2 alpha chain receptor (sCD25) and soluble haptoglobin−hemoglobin receptor. Our results showed that sCD25, SAA-1, and LRG1 had high levels of specificity and sensitivity, as well as an excellent area under the ROC curve (>0.9). Our study provides a serum proteomic analysis that identifies new diagnostic biomarkers in sepsis. SAA-1, sCD25 and LRG1 were able to separate septic from healthy donor, so they could be used together with other clinical and analytical features to improve sepsis diagnosis in children.
Keywords: biomarkers; children; mass spectrometry analysis; proteome; sepsis; septic shock.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of a panel of serum protein markers in early stage of sepsis and its validation in a cohort of patients.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2018 Aug;51(4):465-472. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2016.12.002. Epub 2017 Jun 13. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2018. PMID: 28655573
-
Identification of novel biomarkers for sepsis diagnosis via serum proteomic analysis using iTRAQ-2D-LC-MS/MS.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Jan;36(1):e24142. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24142. Epub 2021 Nov 26. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 34825737 Free PMC article.
-
The novel biomarkers for assessing clinical benefits of continuous renal replacement therapy in pediatric sepsis: a pilot study.Clin Proteomics. 2023 Jan 18;20(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s12014-023-09392-2. Clin Proteomics. 2023. PMID: 36650427 Free PMC article.
-
Translational research and biomarkers in neonatal sepsis.Clin Chim Acta. 2015 Dec 7;451(Pt A):46-64. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2015.01.031. Epub 2015 Feb 4. Clin Chim Acta. 2015. PMID: 25661089 Review.
-
Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012.Crit Care Med. 2013 Feb;41(2):580-637. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31827e83af. Crit Care Med. 2013. PMID: 23353941
Cited by
-
Multilevel omics for the discovery of biomarkers in pediatric sepsis.Pediatr Investig. 2023 Nov 21;7(4):277-289. doi: 10.1002/ped4.12405. eCollection 2023 Dec. Pediatr Investig. 2023. PMID: 38050541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Biofilms on Late-Onset Sepsis: Current Challenges and Emerging Diagnostics and Therapies.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Mar 10;12(3):554. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12030554. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36978421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic Profiling of Early Secreted Proteins in Response to Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Vascular Endothelial Cell EA.hy926 Injury.Biomedicines. 2023 Nov 15;11(11):3065. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11113065. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38002065 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of Serum Leucine-rich Alpha-2 Glycoprotein as a Diagnostic Marker in Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Kobe J Med Sci. 2024 Jan 24;69(4):E122-E128. doi: 10.24546/0100486228. Kobe J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38379274 Free PMC article.
-
Cord blood proteomics identifies biomarkers of early-onset neonatal sepsis.JCI Insight. 2025 Jun 10;10(13):e193826. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.193826. eCollection 2025 Jul 8. JCI Insight. 2025. PMID: 40493423 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singer M., Deutschman C.S., Seymour C.W., Shankar-Hari M., Annane D., Bauer M., Bellomo R., Bernard G.R., Chiche J.-D., Coopersmith C.M., et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3) JAMA. 2016;315:801–810. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Weiss S.L., Peters M.J., Alhazzani W., Agus M.S.D., Flori H.R., Inwald D.P., Nadel S., Schlapbach L.J., Tasker R.C., Argent A.C., et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign International Guidelines for the Management of Septic Shock and Sepsis-Associated Organ Dysfunction in Children. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2020;21:e52–e106. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000002198. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
- US10/02/University of the Basque Country
- SAIO10-PE10BF02, SAIO12-PE12BF002, 2012111052, 2019111056/Basque Government
- Grant PRB3 IPT17/0019/Basque Department of Industry, Tourism and Trade (Etortek and Elkartek programs), the Inno-vation Technology Department of the Bizkaia County, the ProteoRed-ISCIII
- SEV-2016-0644/CIBERehd Network and Severo Ochoa Grant
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

