Cognitive and Adaptive Effects of Early Growth Hormone Treatment in Prader-Willi Syndrome Patients: A Cohort Study
- PMID: 35329918
- PMCID: PMC8955812
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11061592
Cognitive and Adaptive Effects of Early Growth Hormone Treatment in Prader-Willi Syndrome Patients: A Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: Prader-Willi Syndrome (PWS) is a genetically based neurodevelopmental disease characterized by obesity, hyperphagia, and mild to moderate intellectual disability. Treatment with growth hormone (GH) could provide cognitive benefits. The objective of the present study was to compare the cognitive and adaptive performance of 31 patients with genetically confirmed PWS grouped in two cohorts, one treated with GH before 2 years old (Group 1) and the other receiving the treatment later (Group 2).
Method: We compared two variables necessary to diagnose intellectual disability: intellectual performance, using the Weschler scales, and adaptive behavior, using the DABS scale. The scores were analyzed by means of non-parametric statistical tests.
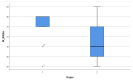
Results: Group 1 (n = 10) obtained higher and statistically significant scores in Total Intelligence Quotient (TIQ), General Ability Index (GAI), and General Adaptive Behavior (GAB), implying better cognitive and adaptive performance compared to Group 2.
Conclusions: Treatment with GH should be administered in the early stage of development (before 2 years old) to obtain greater benefits at the cognitive and adaptive levels.
Keywords: Prader–Willi Syndrome; adaptive behavior; cognition; growth hormone treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gabau E., Aguilera C., Baena N., Ruiz A., Guitart M. Enfermedades por alteración de la impronta genética. Síndrome Prader-Willi y de Angelman. Pediatr. Integral. 2019;XXIII:249–257.
-
- Famelart N., Diene G., Çabal-Berthoumieu S., Glattard M., Molinas C., Guidetti M., Tauber M. Equivocal expression of emotions in children with Prader-Willi syndrome: What are the consequences for emotional abilities and social adjustment? Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020;15:55. doi: 10.1186/s13023-020-1333-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources