Temporomandibular Disk Dislocation Impacts the Stomatognathic System: Comparative Study Based on Biexponential Quantitative T2 Maps
- PMID: 35329946
- PMCID: PMC8953096
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11061621
Temporomandibular Disk Dislocation Impacts the Stomatognathic System: Comparative Study Based on Biexponential Quantitative T2 Maps
Abstract
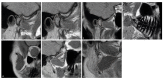
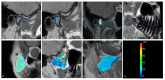
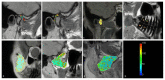
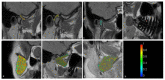
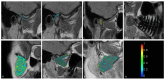
In this study, we aimed to assess the potential impact of temporomandibular disk displacement on anatomical structures of the stomatognathic system using biexponential T2 magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) maps. Fifty separate MRI scans of the temporomandibular joints (TMJ) of 25 patients were acquired with eight echo times. Biexponential T2 maps were created by weighted reconstruction based on Powell's conjugate direction method and divided into two groups: the TMJ without (32 images) and with (18 images) disk displacement. The disk, retrodiscal tissue, condylar bone marrow, masseter muscle, lateral and medial pterygoid muscles and dental pulp of the first and second molars were manually segmented twice. The intrarater reliability was assessed. The averages and standard deviations of the T2 times and fractions of each segmented region for each group were calculated and analysed with multiple Student's t-tests. Significant differences between groups were observed in the retrodiscal tissue, medial pterygoid muscle and bone marrow. The pulp short T2 component showed a trend toward statistical significance. The segmentation reliability was excellent (93.6%). The relationship between disk displacement and quantitative MRI features of stomatognathic structures can be useful in the combined treatment of articular disk displacement, pterygoid muscle tension and occlusive reconstruction.
Keywords: T2 maps; biexponential analysis; quantitative MRI; temporomandibular disk.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pathologic changes of the lateral pterygoid muscle in patients with derangement of the temporomandibular joint disk: objective measures at MR imaging.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007 Sep;28(8):1537-9. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A0590. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007. PMID: 17846207 Free PMC article.
-
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) pain revisited with dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI).Eur J Radiol. 2012 Mar;81(3):603-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2011.01.044. Epub 2011 Feb 5. Eur J Radiol. 2012. PMID: 21300493
-
Evaluation of lateral pterygoid muscle in patients with temporomandibular joint anterior disk displacement using T1-weighted Dixon sequence: a retrospective study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022 Feb 8;23(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12891-022-05079-1. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022. PMID: 35135518 Free PMC article.
-
Temporomandibular joint and masticatory muscle involvement in myotonic dystrophy: a study by magnetic resonance imaging.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002 Aug;94(2):262-71. doi: 10.1067/moe.2002.124580. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002. PMID: 12221397
-
Etiopathogenesis of disk displacement of the temporomandibular joint: a review of the mechanisms.Indian J Dent Res. 2009 Apr-Jun;20(2):212-21. doi: 10.4103/0970-9290.51365. Indian J Dent Res. 2009. PMID: 19553725 Review.
Cited by
-
Photobiomodulation Therapy for the Symptoms Related to Temporomandibular Joint Disk Displacement.Case Rep Dent. 2023 Apr 13;2023:5947168. doi: 10.1155/2023/5947168. eCollection 2023. Case Rep Dent. 2023. PMID: 37089525 Free PMC article.
-
A Weighted Stochastic Conjugate Direction Algorithm for Quantitative Magnetic Resonance Images-A Pattern in Ruptured Achilles Tendon T2-Mapping Assessment.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Apr 23;10(5):784. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10050784. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35627921 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tresoldi M., Dias R., Bracci A., Segù M., Guarda-Nardini L., Manfredini D. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Evaluation of Closed-Mouth TMJ Disc-Condyle Relationship in a Population of Patients Seeking for Temporomandibular Disorders Advice. Pain Res. Manag. 2021:2. doi: 10.1155/2021/5565747. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shokri A., Zarch H.H., Hafezmaleki F., Khamechi R., Amini P., Ramezani L. Comparative assessment of condylar position in patients with temporomandibular disorder (TMD) and asymptomatic patients using cone-beam computed tomography. Dent. Med. Probl. 2019;56:81–87. doi: 10.17219/dmp/102946. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

