Does Far-Infrared Therapy Improve Peritoneal Function and Reduce Recurrent Peritonitis in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients?
- PMID: 35329948
- PMCID: PMC8955287
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11061624
Does Far-Infrared Therapy Improve Peritoneal Function and Reduce Recurrent Peritonitis in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients?
Abstract
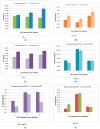
The use of peritoneal dialysis in end-stage renal disease is increasing in clinical practice. The main purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of far-infrared radiation therapy on inflammation and the cellular immunity of patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis. We recruited 56 patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis, and we included 32 patients for the experimental group and 24 patients from the control group in the final analysis. The experimental evaluation in our study was as follows: (1) We used abdominal computed tomography to explore the changes in abdominal blood vessels. (2) We compared the effects of peritoneal dialysis using blood glucose, HbAlC, albumin, urea nitrogen, creatinine, white blood cells, hs-CRP; peritoneal Kt/V of peritoneal function, and eGFR. (3) We compared the cytokines’ concentrations in the two groups while controlling for the other cytokines. Results and Discussion: (1) There was no significant difference in the abdominal blood vessels of the experimental group relative to the control group according to abdominal CT over the 6 months. (2) Our study demonstrates statistically significant effects of FIR therapy on the following parameters: creatinine (p = 0.039 *) and hs-CRP (p < 0.001 **) levels decreased significantly, and eGFR (p = 0.043 *), glucose (p < 0.001 **), and albumin (p = 0.048 *) levels increased significantly. Our study found that in the experimental group, creatinine and hs-CRP levels decreased significantly due to FIR therapy for 6 months. However, our study also found that the glucose level was significantly different after FIR therapy for 6 months. Peritoneal dialysis combined with FIR can reduce the side effects of the glucose in the dialysis buffer, which interferes with peritoneal inflammation and peritoneal mesothelial cell fibrosis. (3) In addition, we also found that no statistically significant difference in any inflammatory cytokine after FIR therapy. IFN-γ (p = 0.124), IL-12p70 (p = 0.093), IL-18 (p = 0.213), and TNF-α (p = 0.254) did not exhibit significant improvements after peritoneal dialysis with FIR treatment over 6 months. Conclusions: We found that the effectiveness of peritoneal dialysis was improved significantly with FIR therapy, and significant improvements in the peritoneal permeability and inflammatory response were observed.
Keywords: end-stage renal disease; far-infrared therapy (FIR); peritoneal dialysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Jamie P.D., Julia B.L. Clinical aspects of diabetic nephropathy. In: Robert W.S., Eric G.N., editors. Schrier’s Diseases of the Kidney. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2012. p. 165975.
-
- Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. Nathan D.M., Genuth S., Lachin J., Cleary P., Crofford O., Davis M., Rand L., Siebert C. The Effect of Intensive Treatment of Diabetes on the Development and Progression of Long-Term Complications in Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993;329:977–986. - PubMed
-
- Yang X., Yu X.Q. Approaches to the protection of peritoneum in patients on long-term peritoneal dialysis. Chin. J. Blood Purif. 2010;9:523–525.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

