Personalized Management and Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 35330211
- PMCID: PMC8951963
- DOI: 10.3390/life12030460
Personalized Management and Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
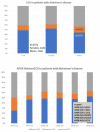
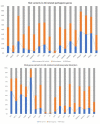
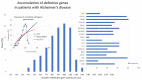
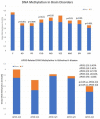
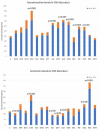
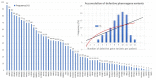
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a priority health problem with a high cost to society and a large consumption of medical and social resources. The management of AD patients is complex and multidisciplinary. Over 90% of patients suffer from concomitant diseases and require personalized therapeutic regimens to reduce adverse drug reactions (ADRs), drug−drug interactions (DDIs), and unnecessary costs. Men and women show substantial differences in their AD-related phenotypes. Genomic, epigenetic, neuroimaging, and biochemical biomarkers are useful for predictive and differential diagnosis. The most frequent concomitant diseases include hypertension (>25%), obesity (>70%), diabetes mellitus type 2 (>25%), hypercholesterolemia (40%), hypertriglyceridemia (20%), metabolic syndrome (20%), hepatobiliary disorder (15%), endocrine/metabolic disorders (>20%), cardiovascular disorder (40%), cerebrovascular disorder (60−90%), neuropsychiatric disorders (60−90%), and cancer (10%). Over 90% of AD patients require multifactorial treatments with risk of ADRs and DDIs. The implementation of pharmacogenetics in clinical practice can help optimize the limited therapeutic resources available to treat AD and personalize the use of anti-dementia drugs, in combination with other medications, for the treatment of concomitant disorders.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; anti-dementia drugs; biomarkers; cerebrovascular genomics; concomitant disorders; neurodegenerative genomics; pathogenic genes; pharmacogenomics; phenotype-modifying treatments.
Conflict of interest statement
RC is President and stockholder of EuroEspes (Biomedical Research Center), EuroEspes Biotechnology, IABRA, and EuroEspes Publishing Co. NC is a shareholder of EuroEspes S.A. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any other organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed apart from those disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacogenomics of Alzheimer's Disease: Novel Strategies for Drug Utilization and Development.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2547:275-387. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2573-6_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 36068470
-
Pharmacogenomics of Alzheimer's disease: novel therapeutic strategies for drug development.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1175:323-556. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-0956-8_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 25150875 Review.
-
Molecular pathology and pharmacogenomics in Alzheimer's disease: polygenic-related effects of multifactorial treatments on cognition, anxiety and depression.Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2007 Jul;29 Suppl A:1-91. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17957277 Review.
-
Pharmacogenomics and therapeutic strategies for dementia.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2009 Sep;9(6):567-611. doi: 10.1586/erm.09.42. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2009. PMID: 19732004 Review.
-
Molecular genetics of Alzheimer's disease and aging.Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2005 Jul;27 Suppl A:1-573. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16470248
Cited by
-
Relationship between antidementia medication and fracture prevention in patients with Alzheimer's dementia using a nationwide health insurance claims database.Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 27;13(1):6893. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-34173-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37106031 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomaterials that Aid in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease, Resolving Blood-Brain Barrier Crossing Ability.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Oct;11(38):e2403473. doi: 10.1002/advs.202403473. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39101248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Options in Alzheimer's Disease: From Classic Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors to Multi-Target Drugs with Pleiotropic Activity.Life (Basel). 2024 Nov 26;14(12):1555. doi: 10.3390/life14121555. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39768263 Free PMC article.
-
Licochalcone A: A Potential Multitarget Drug for Alzheimer's Disease Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 16;24(18):14177. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814177. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes in brain diseases: Pathogenesis and therapeutic targets.MedComm (2020). 2023 Jun 11;4(3):e287. doi: 10.1002/mco2.287. eCollection 2023 Jun. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 37313330 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization Dementia. [(accessed on 3 February 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia.
-
- Cacabelos R., Fernández-Novoa L., Lombardi V., Kubota Y., Takeda M. Molecular genetics of Alzheimer’s disease and aging. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005;27:1–573. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

