Risk Factors for COVID-19 Associated Mucormycosis: The Ophthalmologist's Perspective
- PMID: 35330273
- PMCID: PMC8948853
- DOI: 10.3390/jof8030271
Risk Factors for COVID-19 Associated Mucormycosis: The Ophthalmologist's Perspective
Abstract
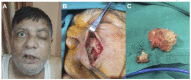
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to a dramatic rise in the incidence of rhino-orbito-cerebral mucormycosis (ROCM) in India. The purpose of our report is to describe the prevalence of ROCM in the context of SARS-CoV-2 infection during the second Indian COVID-19 wave, as well as its diagnostics proceeding, and to discuss the challenges met in the time frame from the suspected diagnosis to the therapeutic decision in such patients. We conducted a retrospective multicentre case series study at six centres of Sudhalkar and Raghudeep group of hospitals in India. ROCM was confirmed in 38 (2.5%) of the 1546 patients admitted with SARS-CoV-2 infection. The average time to establish a diagnosis was 16 days. In total, 19 (50%) patients suffered from type 2 diabetes and were mostly treated with hypoglycaemic agents (in 90% of cases). The standard of care for SARS-CoV-2 management included systemic steroids therapy, intravenous remdesivir for 5 days, and concomitant prophylactic antibiotic therapy following admission. The median (IQR) blood glucose levels in all patients during the course of hospitalisation was 320 (250.5-375) mg/dl. A total of 16% of patients had an irreparable functional loss, and the mortality was 5%. We may hypothesise that excessive administration of antibiotics that profoundly affects human microbiota, coupled with poorly controlled glycaemia and unprotocolised haphazard steroid administration, contribute to a favourable setting for mucormycosis infections.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; fungus; immunosuppression; mucormycosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ak A.K., Gupta V. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2022. Rhino-Orbital Cerebral Mucormycosis. - PubMed
-
- Sen M., Honavar S.G., Bansal R., Sengupta S., Rao R., Kim U., Sharma M., Sachdev M., Grover A.K., Surve A., et al. Epidemiology, Clinical Profile, Management, and Outcome of COVID-19-Associated Rhino-Orbital-Cerebral Mucormycosis in 2826 Patients in India—Collaborative OPAI-IJO Study on Mucormycosis in COVID-19 (COSMIC), Report 1. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2021;69:1670–1692. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_1565_21. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fazeli M.A., Rezaei L., Javadirad E., Iranfar K., Khosravi A., Saman J.A., Poursabbagh P., Ghadami M.R., Parandin M.M., Dehghani A., et al. Increased incidence of rhino-orbital mucormycosis in an educational therapeutic hospital during the COVID-19 pandemic in western Iran: An observational study. Mycoses. 2021;64:1366–1377. doi: 10.1111/myc.13351. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

