Routine Surveillance of Healthcare-Associated Infections Misses a Significant Proportion of Invasive Aspergillosis in Patients with Severe COVID-19
- PMID: 35330275
- PMCID: PMC8954197
- DOI: 10.3390/jof8030273
Routine Surveillance of Healthcare-Associated Infections Misses a Significant Proportion of Invasive Aspergillosis in Patients with Severe COVID-19
Abstract
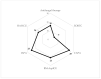
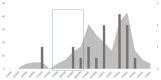
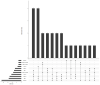
Rates of invasive aspergillosis (IA) among COVID-19 ICU patients seem to reach over 30% in certain settings. At Vienna General Hospital (VGH), all rooms in COVID-19 ICUs were put under negative pressure as a protective measure, thus increasing the risk of exposure to environmental pathogens for patients. Even though all ICU patients are surveilled for healthcare-associated infections (HAI), there were concerns that the routine protocol might not be sufficient for IA detection. We reviewed the electronic patient charts of all patients with COVID-19 admitted to ICUs between 1 March 2020 and 31 July 2021 for fungal co- or superinfections, comparing four diagnostic algorithms based on different recommendations for the diagnosis of IA (according to EORTC/MSG, BM-AspICU, IAPA and CAPA) to our routine surveillance protocol. We found that out of 252 patients who were admitted to the ICU during the study period, 25 (9.9%) fulfilled the criteria of probable or possible IA of at least one algorithm. The IAPA definitions detected 25 and the CAPA definition 23 probable and 2 possible cases, out of which only 16 were classified as hospital-acquired IA by routine surveillance. In conclusion, adjustment of the routine protocol using a classification system especially designed for respiratory viral illness seems useful for the surveillance of IA in a highly vulnerable patient cohort.
Keywords: COVID-19; intensive care; invasive aspergillosis; superinfection; surveillance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Taccone F.S., Abeele A.-M.V.D., Bulpa P., Misset B., Meersseman W., Cardoso T., Paiva J.-A., Blasco-Navalpotro M., De Laere E., Dimopoulos G., et al. Epidemiology of invasive aspergillosis in critically ill patients: Clinical presentation, underlying conditions, and outcomes. Crit. Care. 2015;19:7. doi: 10.1186/s13054-014-0722-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burghi G., Lemiale V., Seguin A., Lambert J., Lacroix C., Canet E., Moreau A.-S., Ribaud P., Schnell D., Mariotte E., et al. Outcomes of mechanically ventilated hematology patients with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Intensive Care Med. 2011;37:1605–1612. doi: 10.1007/s00134-011-2344-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schauwvlieghe A.F.A.D., Rijnders B.J.A., Philips N., Verwijs R., Vanderbeke L., Van Tienen C., Lagrou K., Verweij P.E., Van De Veerdonk F.L., Gommers D., et al. Invasive aspergillosis in patients admitted to the intensive care unit with severe influenza: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018;6:782–792. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(18)30274-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bonnet S., Duléry R., Regany K., Bouketouche M., Magro L., Coiteux V., Alfandari S., Berthon C., Quesnel B., Yakoub-Agha I. Long-term follow up of invasive aspergillosis in allogeneic stem cell transplantation recipients and leukemia patients: Differences in risk factors and outcomes. Curr. Res. Transl. Med. 2017;65:77–81. doi: 10.1016/j.retram.2017.05.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nicolle M.C., Bénet T., Thiebaut A., Bienvenu A.-L., Voirin N., Duclos A., Sobh M., Cannas G., Thomas X., Nicolini F.-E., et al. Invasive aspergillosis in patients with hematologic malignancies: Incidence and description of 127 cases enrolled in a single institution prospective survey from 2004 to 2009. Haematologica. 2011;96:1685–1691. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2011.044636. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

