Searching for New Molecular Targets for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma with a View to Clinical Implementation of Precision Medicine
- PMID: 35330413
- PMCID: PMC8954939
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm12030413
Searching for New Molecular Targets for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma with a View to Clinical Implementation of Precision Medicine
Abstract
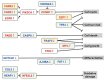
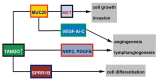
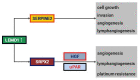
Head and neck cancer, including oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), is the eighth most common malignancy globally and is characterized by local invasiveness and high nodal metastatic potential. The OSCC incidence is also increasing, and the number of deaths is also rising steadily in Japan. The development of molecular markers to eradicate OSCC is an urgent issue for humankind. The increase in OSCC despite the declining smoking rate may be due to several viral infections through various sexual activities and the involvement of previously unfocused carcinogens, and genetic alterations in individual patients are considered to be more complicated. Given this situation, it is difficult to combat OSCC with conventional radiotherapy and chemotherapy using cell-killing anticancer drugs alone, and the development of precision medicine, which aims to provide tailor-made medicine based on the genetic background of each patient, is gaining attention. In this review article, the current status of the comprehensive search for driver genes and biomarkers in OSCC will be briefly described, and some of the candidates for novel markers of OSCC that were found will be outlined.
Keywords: biomarker; oral squamous cell carcinoma; precision medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources