The Morphology of a Kinematically Aligned Distal Femoral Osteotomy Is Different from That Obtained with Mechanical Alignment and Could Have Implications for the Design of Total Knee Arthroplasty
- PMID: 35330422
- PMCID: PMC8955119
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm12030422
The Morphology of a Kinematically Aligned Distal Femoral Osteotomy Is Different from That Obtained with Mechanical Alignment and Could Have Implications for the Design of Total Knee Arthroplasty
Abstract
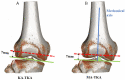
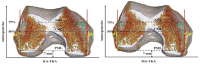
Background: Kinematically aligned total knee arthroplasty (KA-TKA) may lead to a different pattern of osteotomy from mechanically aligned total knee arthroplasty (MA-TKA). This paper aims to analyze the effects of KA and MA on the morphology of the distal femoral osteotomy surface. Methods: Computed tomography scans of 80 TKA candidates were reconstructed into 3D models. The measurement of bone morphology was performed after the distal femur cut according to two different alignment techniques. The aspect ratio, trapezoidicity ratio, and asymmetry ratio of the distal femur were assessed. Results: The aspect ratio and the asymmetry ratio in the KA group was significantly lower than that in the MA group in the general population (p < 0.001). The trapezoidicity ratio in the KA group was significantly higher than that in the MA group in the general population (p < 0.001). Conclusions: It was found that KA-TKA and MA-TKA presented different morphologies of the distal femoral osteotomy surface, and this difference was also influenced by gender. The surgery pattern of KA-TKA and MA-TKA and gender should be considered when surgeons choose femoral prostheses.
Keywords: kinematic alignment; mechanical alignment; morphotype; total knee arthroplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Morphological Patterns of Anterior Femoral Condylar Resection in Kinematically and Mechanically Aligned Total Knee Arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 2018 Aug;33(8):2506-2511. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2018.03.063. Epub 2018 Apr 9. J Arthroplasty. 2018. PMID: 29739631
-
Kinematically Aligned Total Knee Arthroplasty Using Medial Pivot Knee Prosthesis Enhances Medial Pivot Motion: A Comparative Kinematic Study With Mechanically Aligned Total Knee Arthroplasty.Arthroplast Today. 2021 Dec 10;13:24-28. doi: 10.1016/j.artd.2021.10.004. eCollection 2022 Feb. Arthroplast Today. 2021. PMID: 34917717 Free PMC article.
-
Kinematically aligned total knee arthroplasty reproduces more native rollback and laxity than mechanically aligned total knee arthroplasty: A matched pair cadaveric study.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019 Jun;105(4):605-611. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2019.03.011. Epub 2019 Apr 18. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019. PMID: 31006644
-
No difference in postoperative patient satisfaction rates between mechanical and kinematic alignment total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review.J Exp Orthop. 2024 Jul 24;11(3):e12101. doi: 10.1002/jeo2.12101. eCollection 2024 Jul. J Exp Orthop. 2024. PMID: 39050592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of Kinematic Alignment and Mechanical Alignment in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials.Orthop Surg. 2020 Dec;12(6):1567-1578. doi: 10.1111/os.12826. Epub 2020 Oct 25. Orthop Surg. 2020. PMID: 33099892 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beckers L., Müller J.H., Daxhelet J., Ratano S., Saffarini M., Aït-Si-Selmi T., Bonnin M.P. Considerable inter-individual variability of tibial geometric ratios renders bone-implant mismatch unavoidable using off-the-shelf total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2021 doi: 10.1007/s00167-021-06623-7. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

