Whole Brain Hemodynamic Response Based on Synchrony Analysis of Brain Signals for Effective Application of HD-tDCS in Stroke Patients: An fNIRS Study
- PMID: 35330432
- PMCID: PMC8949719
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm12030432
Whole Brain Hemodynamic Response Based on Synchrony Analysis of Brain Signals for Effective Application of HD-tDCS in Stroke Patients: An fNIRS Study
Abstract
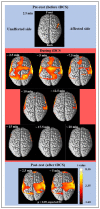
In this study, the effective application of high-definition transcranial direct current stimulation (HD-tDCS) based on the whole brain hemodynamic response in stroke patients was investigated using functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS). The intrahemispheric and interhemispheric synchronization and cortical activity based on the time during 1 mA HD-tDCS were examined in 26 chronic cerebrovascular disease patients. At the beginning of HD-tDCS, the synchronization and brain activity in the whole brain increased rapidly and decreased after 5 min. In the middle of tDCS, the synchronization began to increase again, and strong synchronic connections were formed around the desired stimulation area. After tDCS, strong cortical activation was observed in the stimulation area, indicating that the baseline of the oxyhemoglobin (HbO) signal increased in the desired stimulation area. Therefore, the results of this study indicate that HD-tDCS can be applied efficiently to enhance the effect of tDCS. This stimulation method with tDCS can be explored clinically for more neurorehabilitation of patients with degenerative brain diseases.
Keywords: HD-tDCS; brain signal synchronization; fNIRS; hemodynamic response; stroke patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Alterations in learning-related cortical activation and functional connectivity by high-definition transcranial direct current stimulation after stroke: an fNIRS study.Front Neurosci. 2023 Jun 2;17:1189420. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1189420. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37332855 Free PMC article.
-
Task-Related Hemodynamic Changes Induced by High-Definition Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation in Chronic Stroke Patients: An Uncontrolled Pilot fNIRS Study.Brain Sci. 2022 Mar 28;12(4):453. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12040453. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 35447985 Free PMC article.
-
Focal Hemodynamic Responses in the Stimulated Hemisphere During High-Definition Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation.Neuromodulation. 2018 Jun;21(4):348-354. doi: 10.1111/ner.12632. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Neuromodulation. 2018. PMID: 28714545
-
Systematic review of combined functional near-infrared spectroscopy and transcranial direct-current stimulation studies.Neurophotonics. 2020 Apr;7(2):020901. doi: 10.1117/1.NPh.7.2.020901. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Neurophotonics. 2020. PMID: 32607389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) on Cognitive Performance and Cerebral Oxygen Hemodynamics: A Systematic Review.Front Hum Neurosci. 2021 Apr 7;15:623315. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.623315. eCollection 2021. Front Hum Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33897392 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Neuromodulation with transcranial direct current stimulation contributes to motor function recovery via microglia in spinal cord injury.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 4;14(1):18031. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69127-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39098975 Free PMC article.
-
Resting-state hemodynamic changes and effects on upper limb function after multi-channel transcranial direct current stimulation to the ipsilesional primary motor cortex and anterior intraparietal sulcus in stroke patients: an fNIRS pilot study.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2025 Apr 16;22(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12984-025-01618-8. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2025. PMID: 40241110 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Personalized Approaches to Stroke: One Step Forward for Functional Recovery of Stroke Patients.J Pers Med. 2022 May 19;12(5):822. doi: 10.3390/jpm12050822. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35629244 Free PMC article.
-
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation for Chronic Stroke: Is Neuroimaging the Answer to the Next Leap Forward?J Clin Med. 2023 Mar 30;12(7):2601. doi: 10.3390/jcm12072601. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37048684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of a 12-week tele-exercise program on cognitive function and cerebral oxygenation in patients with OSA: randomized controlled trial-protocol study.Front Sports Act Living. 2024 Sep 6;6:1418439. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2024.1418439. eCollection 2024. Front Sports Act Living. 2024. PMID: 39346497 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
- HI17C1501/by the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea
- NRF-2020R1A2C3010304/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government
- NRF-2019R1I1A1A01060660/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

