Risk of Dementia According to Surgery Type: A Nationwide Cohort Study
- PMID: 35330467
- PMCID: PMC8955036
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm12030468
Risk of Dementia According to Surgery Type: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Abstract
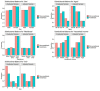
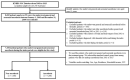
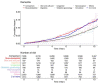
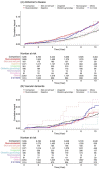
The relationship between dementia and surgery remains unclear. Research to elucidate the relationship between them is scarce, and conducting epidemiological research is complicated. This study aimed to investigate the incidence and risk of dementia according to the surgery type. We performed a retrospective propensity score-matched cohort study using nationwide representative cohort sample data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service in South Korea between 2003 and 2004. Incidence rates for dementia were obtained by dividing the number of patients with dementia by person-years at risk. To identify the risk of dementia according to the type of surgery, we investigated the hazard ratio by each surgery type. The incidence rates of dementia in control, musculoskeletal, and two or more surgeries groups were 9.66, 13.47, and 13.36 cases per 1000 person-years, respectively. The risk of dementia in the musculoskeletal and two or more surgeries groups was 1.44-fold higher (95% confidence interval (95% CI), 1.22-1.70) and 1.42-fold higher (95% CI, 1.17-1.72) than that in the control group, respectively. Patients who underwent musculoskeletal surgery and two or more surgeries had a higher risk of dementia; however, there was no association with the type of anesthesia administered.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; anesthesia; dementia; incidence rate; surgery type; vascular dementia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Risk of Dementia in Patients Who Underwent Surgery under Neuraxial Anesthesia: A Nationwide Cohort Study.J Pers Med. 2021 Dec 20;11(12):1386. doi: 10.3390/jpm11121386. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 34945858 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Burning Mouth Syndrome and the Development of Depression, Anxiety, Dementia, and Parkinson Disease.JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jun 1;146(6):561-569. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2020.0526. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020. PMID: 32352482 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal Study of the Association between General Anesthesia and Increased Risk of Developing Dementia.J Pers Med. 2021 Nov 16;11(11):1215. doi: 10.3390/jpm11111215. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 34834567 Free PMC article.
-
Mortality and morbidity in patients with osteogenesis imperfecta in Denmark.Dan Med J. 2018 Apr;65(4):B5454. Dan Med J. 2018. PMID: 29619932 Review.
-
Depression, stroke, and dementia in patients with myocardial infarction.Dan Med J. 2018 Apr;65(4):B5423. Dan Med J. 2018. PMID: 29619929 Review.
Cited by
-
HSP90 Inhibition Attenuated Isoflurane-Induced Neurotoxicity in Mice and Human Neuroglioma Cells.Neurochem Res. 2024 Mar;49(3):706-717. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-04060-1. Epub 2023 Dec 6. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 38055149
-
Association between surgery and rate of incident dementia in older adults: A population-based retrospective cohort study.J Am Geriatr Soc. 2024 May;72(5):1348-1359. doi: 10.1111/jgs.18736. Epub 2024 Jan 2. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2024. PMID: 38165146 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Chronic Rhinosinusitis on the Risk of Development of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2023 Sep;15(5):647-658. doi: 10.4168/aair.2023.15.5.647. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2023. PMID: 37827981 Free PMC article.
-
Risk of dementia in older patients with different anesthesia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies.BMC Geriatr. 2025 Jul 5;25(1):493. doi: 10.1186/s12877-025-06096-0. BMC Geriatr. 2025. PMID: 40618084 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes, Requirement of Insulin Treatment, and Diabetes-Related Complications among Patients with Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 8;15(4):1094. doi: 10.3390/cancers15041094. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831436 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO Dementia. [(accessed on 2 March 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia.
-
- Shavit Y., Weidenfeld J., DeKeyser F.G., Fish G., Wolf G., Mayburd E., Meerson Y., Beilin B. Effects of surgical stress on brain prostaglandin E2 production and on the pituitary–Adrenal axis: Attenuation by preemptive analgesia and by central amygdala lesion. Brain Res. 2005;1047:10–17. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2005.04.003. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

