Exploring the Cunninghamia lanceolata(Lamb.) Hook Genome by BAC Sequencing
- PMID: 35330626
- PMCID: PMC8940289
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.854130
Exploring the Cunninghamia lanceolata(Lamb.) Hook Genome by BAC Sequencing
Abstract
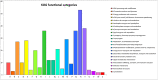
Cunninghamia lanceolata (Lamb.)Hook is an important economic timber tree in China. However, its genome characteristics have not been extensively assessed. To better understand its genome information, the bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) library of chinese fir was constructed. A total of 422 BAC clones were selected and divided into 10 pools and sequenced, and with an average insert size of 121 kb, ranging from 97 to 145 kb. A total of 61,902,523 bp of reference sequences were sequenced and assembled, and based on an estimated genome size of 11.6 Gb for Chinese fir, the BAC library was estimated to have a total coverage of 0.53% genome equivalents. Bioinformatics analyses were also performed for repeated sequences, tRNAs, coding gene prediction, and functional annotation. The results of this study provide insights into the brief structure of the Chinese fir genome and has generated gene data that will facilitate molecular investigations on the mechanisms underlying tree growth.
Keywords: BAC; China; Chinese fir; Cunninghamia lanceolata (lamb.); genome.
Copyright © 2022 Ji, Zhu, Hao, Su, Zheng, Shi, Zheng and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Transcriptome characteristics and six alternative expressed genes positively correlated with the phase transition of annual cambial activities in Chinese Fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata (Lamb.) Hook).PLoS One. 2013 Aug 12;8(8):e71562. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071562. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23951189 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of the Chloroplast Genomic Information of Cunninghamia lanceolata (Lamb.) Hook with Sibling Species from the Genera Cryptomeria D. Don, Taiwania Hayata, and Calocedrus Kurz.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jul 7;17(7):1084. doi: 10.3390/ijms17071084. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27399686 Free PMC article.
-
Genome survey of Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata): Identification of genomic SSRs and demonstration of their utility in genetic diversity analysis.Sci Rep. 2020 Mar 13;10(1):4698. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-61611-0. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32170167 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic Revelation of Phenolic Compounds Involved in Aluminum Toxicity Responses in Roots of Cunninghamia lanceolata (Lamb.) Hook.Genes (Basel). 2019 Oct 23;10(11):835. doi: 10.3390/genes10110835. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31652726 Free PMC article.
-
Tree biomass estimation of Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) based on Bayesian method.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 20;8(11):e79868. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079868. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24278198 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Non-destructive estimation of needle leaf chlorophyll and water contents in Chinese fir seedlings based on hyperspectral reflectance spectra.For Res (Fayettev). 2024 Jul 2;4:e024. doi: 10.48130/forres-0024-0021. eCollection 2024. For Res (Fayettev). 2024. PMID: 39524415 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Duan H., Hu D., Li Y., Zheng H. (2016). Characterization of a Collection of Chinese Fir Elite Genotypes Using Sequence-Related Amplified Polymorphism Markers. J. For. Res. 27 (5), 1105–1110. 10.1007/s11676-016-0233-2 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

