Pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM): A literature overview and case report
- PMID: 35330669
- PMCID: PMC8938872
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2022.02.075
Pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM): A literature overview and case report
Abstract
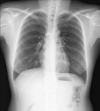
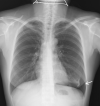
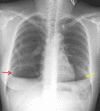
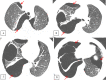
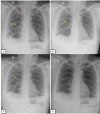
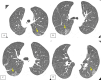
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis is a rare multisystem disease associated with genetic mutations. The disease usually occurs in women of childbearing age and is characterized by infiltration of immature smooth muscle cells into the lungs, airways, and axial lymphatic systems of the chest and abdomen. The disease often destroys lung parenchyma and produces air cysts. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis cell infiltration of the lymphatic axis can affect hilar lymph nodes, mediastinal ganglia, and extrathoracic lymph nodes. The disease can cause lymphatic dilation in the lungs and thoracic ducts, causing chylous effusion into the pleural or abdominal cavities. Invasion of cells into the walls of pulmonary veins can lead to venous obstruction and pulmonary venous hypertension with hemoptysis. Most patients present with cough, dyspnea, pneumothorax, hemoptysis, and abnormal lung function. Definitive diagnosis is usually based on histopathology and immunohistochemistry. We present a case of LAM in a 36-year-old female patient who was confirmed by specimens obtained from pneumothorax surgery and positive immunohistochemical staining with HMB-45.
Keywords: Computed tomography; LAM; Lung lymphangioleiomyomatosis; PEComa.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of University of Washington.
Figures

References
-
- Richard Webb W., Higgins Charles B. Thoracic imaging: pulmonary and cardiovascular radilogy. Wolters Kluwer. 2017;3:649–653.
-
- Richard Webb W., Muller Nestor L., Naidich David P. High – resolution CT of the lung. Wolters Kluwer. 2015;3:501–510.
-
- McCormack FX, Gupta N, Finlay GR, Young LR, Taveira-DaSilva AM, Glasgow CG, et al. ATS/JRS committee on lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Official American thoracic Society/Japanese respiratory society clinical practice guidelines: lymphangioleiomyomatosis diagnosis and management. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;194(6):748–761. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201607-1384ST. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

