A Systematic Review of Candidate miRNAs, Its Targeted Genes and Pathways in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia-An Integrated Bioinformatical Analysis
- PMID: 35330714
- PMCID: PMC8940286
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.848199
A Systematic Review of Candidate miRNAs, Its Targeted Genes and Pathways in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia-An Integrated Bioinformatical Analysis
Abstract
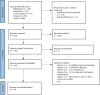
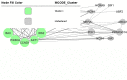
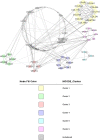
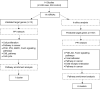
Chronic myeloid leukaemia is blood cancer due to a reciprocal translocation, resulting in a BCR-ABL1 oncogene. Although tyrosine kinase inhibitors have been successfully used to treat CML, there are still cases of resistance. The resistance occurred mainly due to the mutation in the tyrosine kinase domain of the BCR-ABL1 gene. However, there are still many cases with unknown causes of resistance as the etiopathology of CML are not fully understood. Thus, it is crucial to figure out the complete pathogenesis of CML, and miRNA can be one of the essential pathogeneses. The objective of this study was to systematically review the literature on miRNAs that were differentially expressed in CML cases. Their target genes and downstream genes were also explored. An electronic search was performed via PubMed, Scopus, EBSCOhost MEDLINE, and Science Direct. The following MeSH (Medical Subject Heading) terms were used: chronic myeloid leukaemia, genes and microRNAs in the title or abstract. From 806 studies retrieved from the search, only clinical studies with in-vitro experimental evidence on the target genes of the studied miRNAs in CML cells were included. Two independent reviewers independently scrutinised the titles and abstracts before examining the eligibility of studies that met the inclusion criteria. Study design, sample size, sampling type, and the molecular method used were identified for each study. The pooled miRNAs were analysed using DIANA tools, and target genes were analysed with DAVID, STRING and Cytoscape MCODE. Fourteen original research articles on miRNAs in CML were included, 26 validated downstream genes and 187 predicted target genes were analysed and clustered into 7 clusters. Through GO analysis, miRNAs' target genes were localised throughout the cells, including the extracellular region, cytosol, and nucleus. Those genes are involved in various pathways that regulate genomic instability, proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle, differentiation, and migration of CML cells.
Keywords: BCR-ABL1; chronic myeloid leukemia; genes; microRNA; pathways.
Copyright © 2022 Elias, Syed Mohamad and Abdul Hamid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Profiling of miRNAs and their interfering targets in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia.Front Oncol. 2023 Jul 5;13:1173970. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1173970. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37476380 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Candidate Genes and Pathways in Preeclampsia-An Integrated Bioinformatical Analysis.Biology (Basel). 2020 Mar 27;9(4):62. doi: 10.3390/biology9040062. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32230784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-96 acts as a tumor suppressor via targeting the BCR-ABL1 oncogene in chronic myeloid leukemia blastic transformation.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Nov;119:109413. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109413. Epub 2019 Sep 10. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31518872
-
New Developments in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Implications for Therapy.Iran J Cancer Prev. 2016 Feb 22;9(1):e3961. doi: 10.17795/ijcp-3961. eCollection 2016 Feb. Iran J Cancer Prev. 2016. PMID: 27366312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global identification of circular RNAs in imatinib (IM) resistance of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) by modulating signaling pathways of circ_0080145/miR-203/ABL1 and circ 0051886/miR-637/ABL1.Mol Med. 2021 Nov 15;27(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s10020-021-00395-z. Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34781898 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Dysregulated MicroRNAs in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.Cureus. 2024 Sep 6;16(9):e68770. doi: 10.7759/cureus.68770. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39376808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Mechanism of Anti-Tumor Activity of 6-Morpholino- and 6-Amino-9-Sulfonylpurine Derivatives on Human Leukemia Cells.Molecules. 2023 Aug 19;28(16):6136. doi: 10.3390/molecules28166136. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37630388 Free PMC article.
-
The miRNA Landscape of Leukemia - Cellular Actions to Therapy through Molecular Mechanisms.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Jul 18. doi: 10.1007/s12013-025-01820-4. Online ahead of print. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 40679764 Review.
-
Role of miRNAs to control the progression of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia by their expression levels.Med Oncol. 2024 Jan 12;41(2):55. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02278-1. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38216843 Review.
-
Evaluation of MicroRNA as Minimal Residual Disease in Leukemia: Diagnostic and Prognostic Approach: A Review.Iran J Public Health. 2023 Dec;52(12):2541-2553. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v52i12.14315. Iran J Public Health. 2023. PMID: 38435763 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cilloni D, Saglio G. Molecular Pathways: BCR-ABL. Clin Cancer Res (2012) 18(4):930–7. - PubMed
-
- Zhu X, Zhao H, Lin Z, Zhang G. Functional Studies of miR-130a on the Inhibitory Pathways of Apoptosis in Patients With Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Gene Ther (2015) 22(12):573–80. - PubMed
-
- Hershkovitz-Rokah O, Modai S, Pasmanik-Chor M, Toren A, Shomron N, Raanani P, et al. . Restoration of miR-424 Suppresses BCR-ABL Activity and Sensitizes CML Cells to Imatinib Treatment. Cancer Lett (2015) 360(2):245–56. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

