A Necroptosis-Related lncRNA-Based Signature to Predict Prognosis and Probe Molecular Characteristics of Stomach Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 35330731
- PMCID: PMC8940523
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.833928
A Necroptosis-Related lncRNA-Based Signature to Predict Prognosis and Probe Molecular Characteristics of Stomach Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
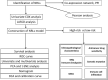
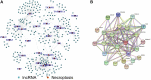
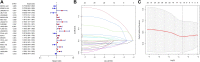
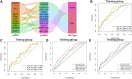
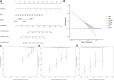
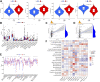
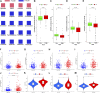
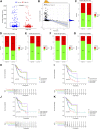
Background: As a caspase-independent type of cell death, necroptosis plays a significant role in the initiation, and progression of gastric cancer (GC). Numerous studies have confirmed that long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are closely related to the prognosis of patients with GC. However, the relationship between necroptosis and lncRNAs in GC remains unclear. Methods: The molecular profiling data (RNA-sequencing and somatic mutation data) and clinical information of patients with stomach adenocarcinoma (STAD) were retrieved from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. Pearson correlation analysis was conducted to identify the necroptosis-related lncRNAs (NRLs). Subsequently, univariate Cox regression and LASSO-Cox regression were conducted to establish a 12-NRLs signature in the training set and validate it in the testing set. Finally, the prognostic power of the 12-NRLs signature was appraised via survival analysis, nomogram, Cox regression, clinicopathological characteristics correlation analysis, and the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Furthermore, correlations between the signature risk score (RS) and immune cell infiltration, immune checkpoint molecules, somatic gene mutations, and anticancer drug sensitivity were analyzed. Results: In the present study, a 12-NRLs signature comprising REPIN1-AS1, UBL7-AS1, LINC00460, LINC02773, CHROMR, LINC01094, FLNB-AS1, ITFG1-AS1, LASTR, PINK1-AS, LINC01638, and PVT1 was developed to improve the prognosis prediction of STAD patients. Unsupervised methods, including principal component analysis and t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding, confirmed the capability of the present signature to separate samples with RS. Kaplan-Meier and ROC curves revealed that the signature had an acceptable predictive potency in the TCGA training and testing sets. Cox regression and stratified survival analysis indicated that the 12-NRLs signature were risk factors independent of various clinical parameters. Additionally, immune cell infiltration, immune checkpoint molecules, somatic gene mutations, and half-inhibitory concentration differed significantly among different risk subtypes, which implied that the signature could assess the clinical efficacy of chemotherapy and immunotherapy. Conclusion: This 12-NRLs risk signature may help assess the prognosis and molecular features of patients with STAD and improve treatment modalities, thus can be further applied clinically.
Keywords: lncRNA; molecular characteristics; necroptosis; prognosis; signature; stomach adenocarcinoma.
Copyright © 2022 Luo, Li, Liu, Feng, Zeng, Shu, Cao and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

