Hydrogen Sulfide Upregulates Acid-sensing Ion Channels via the MAPK-Erk1/2 Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 35330812
- PMCID: PMC8833866
- DOI: 10.1093/function/zqab007
Hydrogen Sulfide Upregulates Acid-sensing Ion Channels via the MAPK-Erk1/2 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) emerged recently as a new gasotransmitter and was shown to exert cellular effects by interacting with proteins, among them many ion channels. Acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs) are neuronal voltage-insensitive Na+ channels activated by extracellular protons. ASICs are involved in many physiological and pathological processes, such as fear conditioning, pain sensation, and seizures. We characterize here the regulation of ASICs by H2S. In transfected mammalian cells, the H2S donor NaHS increased the acid-induced ASIC1a peak currents in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. Similarly, NaHS potentiated also the acid-induced currents of ASIC1b, ASIC2a, and ASIC3. An upregulation induced by the H2S donors NaHS and GYY4137 was also observed with the endogenous ASIC currents of cultured hypothalamus neurons. In parallel with the effect on function, the total and plasma membrane expression of ASIC1a was increased by GYY4137, as determined in cultured cortical neurons. H2S also enhanced the phosphorylation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (pErk1/2), which belongs to the family of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs). Pharmacological blockade of the MAPK signaling pathway prevented the GYY4137-induced increase of ASIC function and expression, indicating that this pathway is required for ASIC regulation by H2S. Our study demonstrates that H2S regulates ASIC expression and function, and identifies the involved signaling mechanism. Since H2S shares several roles with ASICs, as for example facilitation of learning and memory, protection during seizure activity, and modulation of nociception, it may be possible that H2S exerts some of these effects via a regulation of ASIC function.
Keywords: ASIC; MAPK; hydrogen sulfide; p-Erk1/2; patch-clamp; regulation.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of American Physiological Society.
Figures




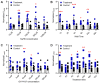
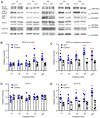
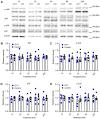

Comment in
-
Hydrogen Sulfide, an Emerging Regulator of Acid-Sensing Ion Channels.Function (Oxf). 2021 Mar 15;2(2):zqab014. doi: 10.1093/function/zqab014. eCollection 2021. Function (Oxf). 2021. PMID: 35330814 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Modulation of acid-sensing ion channels by hydrogen sulfide.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Jun 18;527(1):71-75. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.04.092. Epub 2020 Apr 25. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 32446393
-
Functional characterization of acid-sensing ion channels in cultured neurons of rat inferior colliculus.Neuroscience. 2008 Jun 23;154(2):461-72. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.03.040. Epub 2008 Mar 26. Neuroscience. 2008. PMID: 18456416
-
C-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Post-Translational Regulation of Pain-Related Acid-Sensing Ion Channels 1b and 3.J Neurosci. 2021 Oct 20;41(42):8673-8685. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0570-21.2021. Epub 2021 Aug 11. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34380759 Free PMC article.
-
Acid-Sensing Ion Channels and Mechanosensation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 1;22(9):4810. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094810. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34062742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acid-Sensing Ion Channels: Focus on Physiological and Some Pathological Roles in the Brain.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021;19(9):1570-1589. doi: 10.2174/1570159X19666210125151824. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33550975 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Signaling Pathways in Proton and Non-proton ASIC1a Activation.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Oct 5;15:735414. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.735414. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34675777 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen sulfide and its potential as a possible therapeutic agent in male reproduction.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 11;15:1427069. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1427069. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39324123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic effects of tetrahedral framework nucleic acids and tFNAs-miR22 on retinal ischemia/reperfusion injury.Cell Prolif. 2024 Nov;57(11):e13695. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13695. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Cell Prolif. 2024. PMID: 39086110 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of ASIC1a by reactive oxygen species through JFK signaling.Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 15;14(4):276-280. eCollection 2022. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36161255 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Hydrogen Sulfide, an Emerging Regulator of Acid-Sensing Ion Channels.Function (Oxf). 2021 Mar 15;2(2):zqab014. doi: 10.1093/function/zqab014. eCollection 2021. Function (Oxf). 2021. PMID: 35330814 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Waldmann R, Champigny G, Bassilana F, Heurteaux C, Lazdunski M.. A proton-gated cation channel involved in acid-sensing. Nature 1997;386 (6621):173–177. - PubMed
-
- Kellenberger S, Schild L.. Epithelial sodium channel/degenerin family of ion channels: a variety of functions for a shared structure. Physiol Rev 2002;82 (3):735–767. - PubMed
-
- Bassler EL, Ngo-Anh TJ, Geisler HS, Ruppersberg JP, Grunder S.. Molecular and functional characterization of acid-sensing ion channel (ASIC) 1b. J Biol Chem 2001;276(36):33782–33787. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
