Uncovering the Pharmacological Mechanisms of Gexia-Zhuyu Formula (GXZY) in Treating Liver Cirrhosis by an Integrative Pharmacology Strategy
- PMID: 35330838
- PMCID: PMC8940433
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.793888
Uncovering the Pharmacological Mechanisms of Gexia-Zhuyu Formula (GXZY) in Treating Liver Cirrhosis by an Integrative Pharmacology Strategy
Abstract
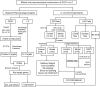
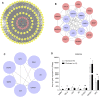
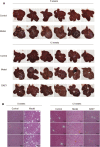
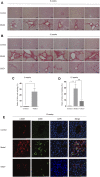
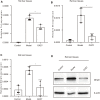
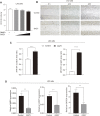
Liver cirrhosis (LC) is a fibrotic lesion of liver tissue caused by the repeated progression of chronic hepatitis. The traditional Chinese medicine Gexia-Zhuyu formula (GXZY) has a therapeutic effect on LC. However, its pharmacological mechanisms on LC remain elucidated. Here, we used the network pharmacology approach to explore the action mechanisms of GXZY on LC. The compounds of GXZY were from the traditional Chinese medicine systems pharmacology (TCMSP) database, and their potential targets were from SwissTargetPrediction and STITCH databases. The disease targets of LC came from GeneCards, DisGeNET, NCBI gene, and OMIM databases. Then we constructed the protein-protein interaction (PPI) network to obtain the key target genes. And the gene ontology (GO), pathway enrichment, and expression analysis of the key genes were also performed. Subsequently, the potential action mechanisms of GXZY on LC predicted by the network pharmacology analyses were experimentally validated in LC rats and LX2 cells. A total of 150 components in GXZY were obtained, among which 111 were chosen as key compounds. The PPI network included 525 targets, and the key targets were obtained by network topological parameters analysis, whereas the predicted key genes of GXZY on LC were AR, JUN, MYC, CASP3, MMP9, GAPDH, and RELA. Furthermore, these key genes were related to pathways in cancer, hepatitis B, TNF signaling pathway, and MAPK signaling pathway. The in vitro and in vivo experiments validated that GXZY inhibited the process of LC mainly via the regulation of cells proliferation and migration through reducing the expression of MMP9. In conclusion, through the combination of network pharmacology and experimental verification, this study offered more insight molecular mechanisms of GXZY on LC.
Keywords: Gexia-Zhuyu formula; liver cirrhosis; network pharmacology; pharmacological mechanisms; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2022 Cao, Liang, Liu, Zao, Zhang, Chen, Liu, Chen, He, Zhang and Ye.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Mechanism of Shaofu Zhuyu Decoction in treatment of EMT induced dysmenorrhea based on network pharmacology and molecular docking].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Dec;46(24):6484-6492. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210816.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34994141 Chinese.
-
[Mechanism of Xuefu Zhuyu Decoction in treatment of myocardial infarction based on network pharmacology and molecular docking].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Feb;46(4):885-893. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20201106.402. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 33645093 Chinese.
-
Network pharmacology and in vitro studies reveal the pharmacological effects and molecular mechanisms of Shenzhi Jiannao prescription against vascular dementia.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Feb 2;22(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03465-1. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 35109845 Free PMC article.
-
[Mechanism of Carthami Flos and Lepidii Semen drug pair in inhibition of myocardial fibrosis by improving cardiac microenvironment based on network pharmacology and animal experiment].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 Feb;47(3):753-763. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210929.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35178959 Chinese.
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Zisheng Shenqi decoction against gout arthritis using network pharmacology.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Feb;90:107358. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107358. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33243703 Review.
Cited by
-
Detecting potential mechanism of vitamin D in treating rheumatoid arthritis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 30;13:1047061. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1047061. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36532774 Free PMC article.
-
The Biological Interaction of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Osteoporosis: A Preliminary Study.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 May 11;10:917907. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.917907. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35646907 Free PMC article.
-
Potential protective benefits of Schisandrin B against severe acute hepatitis in children during the COVID-19 pandemic based on a network pharmacology analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 11;13:969709. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.969709. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36034788 Free PMC article.
-
Application of network pharmacology in traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of digestive system diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 17;15:1412997. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1412997. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39086391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced In Vitro Efficacy of Verbascoside in Suppressing Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation via ROS Scavenging with Reverse Microemulsion.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jul 27;13(8):907. doi: 10.3390/antiox13080907. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199153 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boya P., Larrea E., Sola I., Majano P. L., Jiménez C., Civeira M. P., et al. (2001). Nuclear Factor-Kappa B in the Liver of Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C: Decreased RelA Expression Is Associated with Enhanced Fibrosis Progression. Hepatology 34 (5), 1041–1048. 10.1053/jhep.2001.29002 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

