High Levels of Cerebrospinal Fluid Kappa Free Light Chains Relate to IgM Intrathecal Synthesis and Might Have Prognostic Implications in Relapsing Multiple Sclerosis
- PMID: 35330910
- PMCID: PMC8940299
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.827738
High Levels of Cerebrospinal Fluid Kappa Free Light Chains Relate to IgM Intrathecal Synthesis and Might Have Prognostic Implications in Relapsing Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
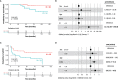
Cerebrospinal kappa free light chain (KFLC)-index is a marker of intrathecal immunoglobulin synthesis that aids in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis (MS). However, little evidence exists on its prognostic role. Our aim is to analyze the relationship between KFLC-index and other MS biomarkers and to explore its prognostic role. This is a monocentric observational study in a cohort of 52 people with relapsing MS (pwRMS) performed on prospectively acquired clinical data and with retrospective evaluation of biomarkers. We measured KFLC-index, immunoglobulin intrathecal synthesis, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) chitinase 3-like 1 (CHI3L1), and neurofilament light protein (NFL) and reviewed MRI to detect leptomeningeal contrast enhancement (LMCE). We compared time to Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) 3 and to initiation of high-efficacy disease-modifying therapies (heDMTs) by multivariate Cox regression analysis. Median KFLC-index correlated with IgG/IgM indexes (p < 0.0001/p < 0.05) and IgG-oligoclonal bands (OCGBs) (p < 0.001). Patients with IgM-oligoclonal bands (OCMBs) had a higher KFLC-index (p = 0.049). KFLC-index was higher in patients with LMCE (p = 0.008) and correlated with CHI3L1 (p = 0.007), but disease activity had no effect on its value. Bivariate and multivariate analyses confirmed KFLC-index > 58 as an independent risk factor for reaching an EDSS of 3 (hazard ratio (HR) = 12.4; 95% CI = 1.1-147; p = 0.047) and for the need of treatment with heDMTs (HR = 3.0; 95% CI = 1.2-7.1; p = 0.0013). To conclude, our data suggest a potential prognostic role of the KFLC-index during the MS course.
Keywords: CHI3L1; ectopic lymphoid follicles; high-efficacy disease-modifying therapies; oligoclonal band; prognostic factor.
Copyright © 2022 Castillo-Villalba, Gil-Perotín, Gasque-Rubio, Cubas-Nuñez, Carratalà-Boscà, Alcalá, Quintanilla-Bordás, Pérez-Miralles, Ferrer, Cañada Martínez, Tortosa, Solís-Tarazona, Campos, Leivas, Laíz Marro and Casanova.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors LC and AL were employed by The Binding Site Iberia. The Binding Site has ceded the turbidimetry kits to measure KFLC for the present study. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

