Kv1.3 Channel Inhibition Limits Uremia-Induced Calcification in Mouse and Human Vascular Smooth Muscle
- PMID: 35330975
- PMCID: PMC8788811
- DOI: 10.1093/function/zqaa036
Kv1.3 Channel Inhibition Limits Uremia-Induced Calcification in Mouse and Human Vascular Smooth Muscle
Abstract
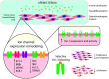
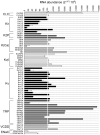
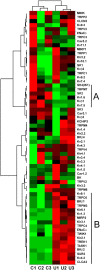
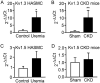
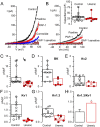
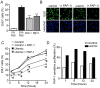
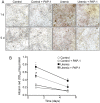
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) significantly increases cardiovascular risk. In advanced CKD stages, accumulation of toxic circulating metabolites and mineral metabolism alterations triggers vascular calcification, characterized by vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) transdifferentiation and loss of the contractile phenotype. Phenotypic modulation of VSMC occurs with significant changes in gene expression. Even though ion channels are an integral component of VSMC function, the effects of uremia on ion channel remodeling has not been explored. We used an in vitro model of uremia-induced calcification of human aorta smooth muscle cells (HASMCs) to study the expression of 92 ion channel subunit genes. Uremic serum-induced extensive remodeling of ion channel expression consistent with loss of excitability but different from the one previously associated with transition from contractile to proliferative phenotypes. Among the ion channels tested, we found increased abundance and activity of voltage-dependent K+ channel Kv1.3. Enhanced Kv1.3 expression was also detected in aorta from a mouse model of CKD. Pharmacological inhibition or genetic ablation of Kv1.3 decreased the amount of calcium phosphate deposition induced by uremia, supporting an important role for this channel on uremia-induced VSMC calcification.
Keywords: BK channels; chronic kidney disease; ion channel remodeling; phenotypic switch; voltage-dependent potassium channels.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of American Physiological Society.
Figures



Comment in
-
Kv1.3 Channel, a Targetable Piece in the Complex Jigsaw Puzzle of Vascular Calcification?Function (Oxf). 2020 Dec 28;2(1):zqaa049. doi: 10.1093/function/zqaa049. eCollection 2021. Function (Oxf). 2020. PMID: 35330970 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Tonelli M, Pfeffer MA.. Kidney disease and cardiovascular risk. Annu Rev Med 2007;58:123–39. - PubMed
-
- Benz K, Varga I, Neureiter D, et al. Vascular inflammation and media calcification are already present in early stages of chronic kidney disease. Cardiovasc Pathol 2017;27:57–67. - PubMed
-
- Moe SM, Chen NX.. Pathophysiology of vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. Circ Res 2004;95(6):560–7. - PubMed
-
- Chen NX, Duan D, O'Neill KD, et al. The mechanisms of uremic serum-induced expression of bone matrix proteins in bovine vascular smooth muscle cells. Kidney Int 2006;70(6):1046–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

