Nanocarrier cancer therapeutics with functional stimuli-responsive mechanisms
- PMID: 35331246
- PMCID: PMC8944113
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-022-01364-2
Nanocarrier cancer therapeutics with functional stimuli-responsive mechanisms
Abstract
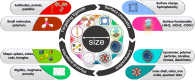
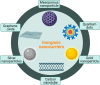
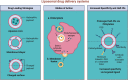
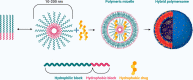
Presently, nanocarriers (NCs) have gained huge attention for their structural ability, good biocompatibility, and biodegradability. The development of effective NCs with stimuli-responsive properties has acquired a huge interest among scientists. When developing drug delivery NCs, the fundamental goal is to tackle the delivery-related problems associated with standard chemotherapy and to carry medicines to the intended sites of action while avoiding undesirable side effects. These nanocarriers were able of delivering drugs to tumors through regulating their pH, temperature, enzyme responsiveness. With the use of nanocarriers, chemotherapeutic drugs could be supplied to tumors more accurately that can equally encapsulate and deliver them. Material carriers for chemotherapeutic medicines are discussed in this review keeping in viewpoint of the structural properties and targeting methods that make these carriers more therapeutically effective, in addition to metabolic pathways triggered by drug-loaded NCs. Largely, the development of NCs countering to endogenous and exogenous stimuli in tumor regions and understanding of mechanisms would encourage the progress for tumor therapy and precision diagnosis in future.
Keywords: Cancer therapy; Functional nanocarriers; Smart drug delivery; Stimulus-responsive drug release.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

