Mutational analysis of compound heterozygous mutation p.Q6X/p.H232R in SRD5A2 causing 46,XY disorder of sex development
- PMID: 35331321
- PMCID: PMC8944008
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-022-01243-4
Mutational analysis of compound heterozygous mutation p.Q6X/p.H232R in SRD5A2 causing 46,XY disorder of sex development
Abstract
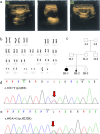
Background: Over 100 mutations in the SRD5A2 gene have been identified in subjects with 46,XY disorder of sex development (DSD). Exploration of SRD5A2 mutations and elucidation of the molecular mechanisms behind their effects should reveal the functions of the domains of the 5α-reductase 2 enzyme and identify the cause of 46,XY DSD. Previously, we reported a novel compound heterozygous p.Q6X/p.H232R mutation of the SRD5A2 gene in a case with 46,XY DSD. Whether the compound heterozygous p.Q6X/p.H232R mutation in this gene causes 46,XY DSD requires further exploration.
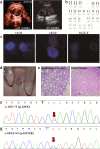
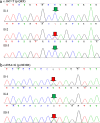
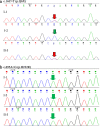
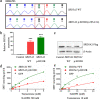
Methods: The two 46,XY DSD cases were identified and sequenced. In order to identify the source of the compound heterozygous p.Q6X/p.H232R mutation, the parents, maternal grandparents, and maternal uncle were sequenced. Since p.Q6X mutation is a nonsense mutation, p.H232R mutation was transfected into HEK293 cells and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) production were analyzed by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) for 5α-reductase 2 enzyme activities test. Apparent michaelis constant (Km) were measured of p.H232R mutation to analyze the binding ability change of 5α-reductase 2 enzyme with testosterone (T) or NADPH.
Results: The sequence results showed that the two 46,XY DSD cases were the compound heterozygous p.Q6X/p.H232R mutation, of which the heterozygous p.Q6X mutation originating from maternal family and heterozygous p.H232R mutation originating from the paternal family. The function analysis confirmed that p.H232R variant decreased the DHT production by LC-MS test. The Km analysis demonstrated that p.H232R mutation affected the binding of SRD5A2 with T or NADPH.
Conclusions: Our findings confirmed that the compound heterozygous p.Q6X/p.H232R mutation in the SRD5A2 gene is the cause of 46,XY DSD. p.H232R mutation reduced DHT production while attenuating the catalytic efficiency of the 5α-reductase 2 enzyme.
Keywords: 46,XY DSD; 5α-reductase 2 catalytic efficiency; Dihydrotestosterone; SRD5A2; p.Q6X/p.H232R mutation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mutations in AR or SRD5A2 Genes: Clinical Findings, Endocrine Pitfalls, and Genetic Features of Children with 46,XY DSD.J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2022 Jun 7;14(2):153-171. doi: 10.4274/jcrpe.galenos.2022.2021-9-19. Epub 2022 Feb 9. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 35135181 Free PMC article.
-
Novel mutations of the SRD5A2 and AR genes in Thai patients with 46, XY disorders of sex development.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Jan 1;30(1):19-26. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2016-0048. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2017. PMID: 27849622
-
Clinical and molecular characterization of 5α-reductase type 2 deficiency due to mutations (p.Q6X, p.R246Q) in SRD5A2 gene.Endocr J. 2018 Jun 27;65(6):645-655. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ17-0542. Epub 2018 Apr 10. Endocr J. 2018. PMID: 29643321
-
The Molecular Basis of 5α-Reductase Type 2 Deficiency.Sex Dev. 2022;16(2-3):171-183. doi: 10.1159/000525119. Epub 2022 Jul 6. Sex Dev. 2022. PMID: 35793650 Review.
-
Diagnosis of 5α-reductase 2 deficiency: is measurement of dihydrotestosterone essential?Clin Chem. 2013 May;59(5):798-806. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2012.196501. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Clin Chem. 2013. PMID: 23513070 Review.
Cited by
-
[Value of the human chorionic gonadotropin stimulation test in the diagnosis of disorder of sexual development in children].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Feb 15;26(2):158-163. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2309090. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38436313 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Evolution, classification, structure, and functional diversification of steroid 5α-reductase family in eukaryotes.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 8;10(14):e34322. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34322. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39108866 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berglund A, Johannsen TH, Stochholm K, Viuff MH, Fedder J, Main KM, et al. Morbidity, Mortality, and Socioeconomics in Females With 46, XY Disorders of Sex Development: A Nationwide Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(4):1418–28. - PubMed
-
- Mongan NP, Tadokoro-Cuccaro R, Bunch T, Hughes IA. Androgen insensitivity syndrome. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;29(4):569–80. - PubMed
-
- Fabbri-Scallet H, de Mello MP, Guerra-Junior G, Maciel-Guerra AT, de Andrade JGR, de Queiroz CMC, et al. Functional characterization of five NR5A1 gene mutations found in patients with 46, XY disorders of sex development. Hum Mutat. 2018;39(1):114–23. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

