Assessing and utilizing esterase specificity in antimicrobial prodrug development
- PMID: 35331374
- PMCID: PMC9033612
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.mie.2021.11.008
Assessing and utilizing esterase specificity in antimicrobial prodrug development
Abstract
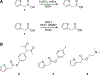
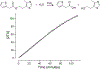
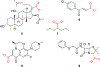
As a class of enzymes, esterases have been investigated for decades and have found use in industrial processes, synthetic organic chemistry, and elsewhere. Esters are functional groups composed of an alcohol moiety and a carboxylic acid moiety. Although much work has explored the influence of the carboxyl moiety of an ester on its susceptibility to esterases, little work has explored the influence of the alcohol moiety. Here, we describe an in vitro methodology to explore the influence of changing the alcohol moiety of an ester on its enzymatic hydrolysis, including strategies for analyzing such data. We then describe leveraging data from these assays to develop targeted antimicrobial prodrugs that activate in certain species due to the discriminatory activity of species-specific esterases. We envisage the potential of genomics and machine learning to further these efforts. Finally, we anticipate the potential future uses of these ideas, including developing targeted anti-cancer compounds.
Keywords: Antimicrobial compounds; Data visualization; Esterases; Genomics; Prodrugs; Targeted therapeutics.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Endogenous Enzymes Enable Antimicrobial Activity.ACS Chem Biol. 2021 May 21;16(5):800-805. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.0c00894. Epub 2021 Apr 20. ACS Chem Biol. 2021. PMID: 33877811 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial esterases and ester prodrugs: An unlikely marriage for combating antibiotic resistance.Drug Dev Res. 2019 Feb;80(1):33-47. doi: 10.1002/ddr.21468. Epub 2018 Oct 10. Drug Dev Res. 2019. PMID: 30302779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure-guided microbial targeting of antistaphylococcal prodrugs.Elife. 2021 Jul 19;10:e66657. doi: 10.7554/eLife.66657. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34279224 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating lipophilicity of rohitukine via prodrug approach: Preparation, characterization, and in vitro enzymatic hydrolysis in biorelevant media.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2016 Sep 20;92:203-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2016.07.010. Epub 2016 Jul 12. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2016. PMID: 27422078
-
Novel approaches for designing 5'-O-ester prodrugs of 3'-azido-2', 3'-dideoxythymidine (AZT).Curr Med Chem. 2000 Oct;7(10):995-1039. doi: 10.2174/0929867003374372. Curr Med Chem. 2000. PMID: 10911016 Review.
Cited by
-
Abridgement of Microbial Esterases and Their Eminent Industrial Endeavors.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Mar;67(3):817-833. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01108-7. Epub 2024 Mar 9. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 38461181 Review.
-
Shifting Mycobacterial Serine Hydrolase Activity Visualized Using Multi-Layer In-Gel Activity Assays.Molecules. 2024 Jul 18;29(14):3386. doi: 10.3390/molecules29143386. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39064965 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian Esterase Activity: Implications for Peptide Prodrugs.Biochemistry. 2024 Oct 15;63(20):2580-2593. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.4c00446. Epub 2024 Oct 3. Biochemistry. 2024. PMID: 39359146 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amarappa S, and Sathyanarayana SV (2014). Data classification using support vector machine (SVM), a simplified approach. Int. J. Electron. Comput. Sci. Eng. 3, 435–445.
-
- Anderson J, Byrne T, Woelfel KJ, Meany JE, Spyridis GT, and Pocker Y (1994). The hydrolysis of p-nitrophenyl acetate: A versatile reaction to study enzyme kinetics. J. Chem. Educ. 71, 715–718.
-
- Bassett B, Waibel B, White A, Hansen H, Stephens D, Koelper A, Larsen EM, Kim C, Glanzer A, Lavis LD, Hoops GC, and Johnson RJ (2018). Measuring the global substrate specificity of mycobacterial serine hydrolases using a library of fluorogenic ester substrates. ACS Infect. Dis. 4, 904–911. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bisswanger H (2014). Enzyme assays. Perspect. Sci. 1, 41–55.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

